Email spoofing is a deceptive technique used by cybercriminals in spam and phishing attacks to deceive users into thinking an email is from a reliable source, using fraudulent headers and sender addresses to make their message look authentic and convince victims into clicking malicious links, downloading malware attachments or providing sensitive data without their knowledge.
With email communication becoming ever more essential to our lives, so does its potential threat. Do you have knowledge of safeguarding yourself against the constantly changing threat of cybersecurity and outsmarting cyber criminals?
History of Email Spoofing

Email spoofing, a deceptive technique employed in spam and phishing attacks, has a long history from the 1970s. As the use of email for communication began to rise, cybercriminals discovered ways to exploit this digital medium for their malicious intents. However, it was in the 2000s that email spoofing emerged as a significant global cybersecurity issue, affecting individuals, businesses, and organizations worldwide.
In response to the growing threat of email spoofing, security protocols were introduced in 2014 to combat this nefarious practice. These protocols aimed to enhance the security of email systems and provide measures to redirect spoofed emails to spam boxes or reject them before they reached the intended recipients' inboxes. Introducing these protocols marked an important milestone in the ongoing battle against email spoofing and phishing attempts.
Understanding Email Spoofing Techniques
Manipulating Email Headers
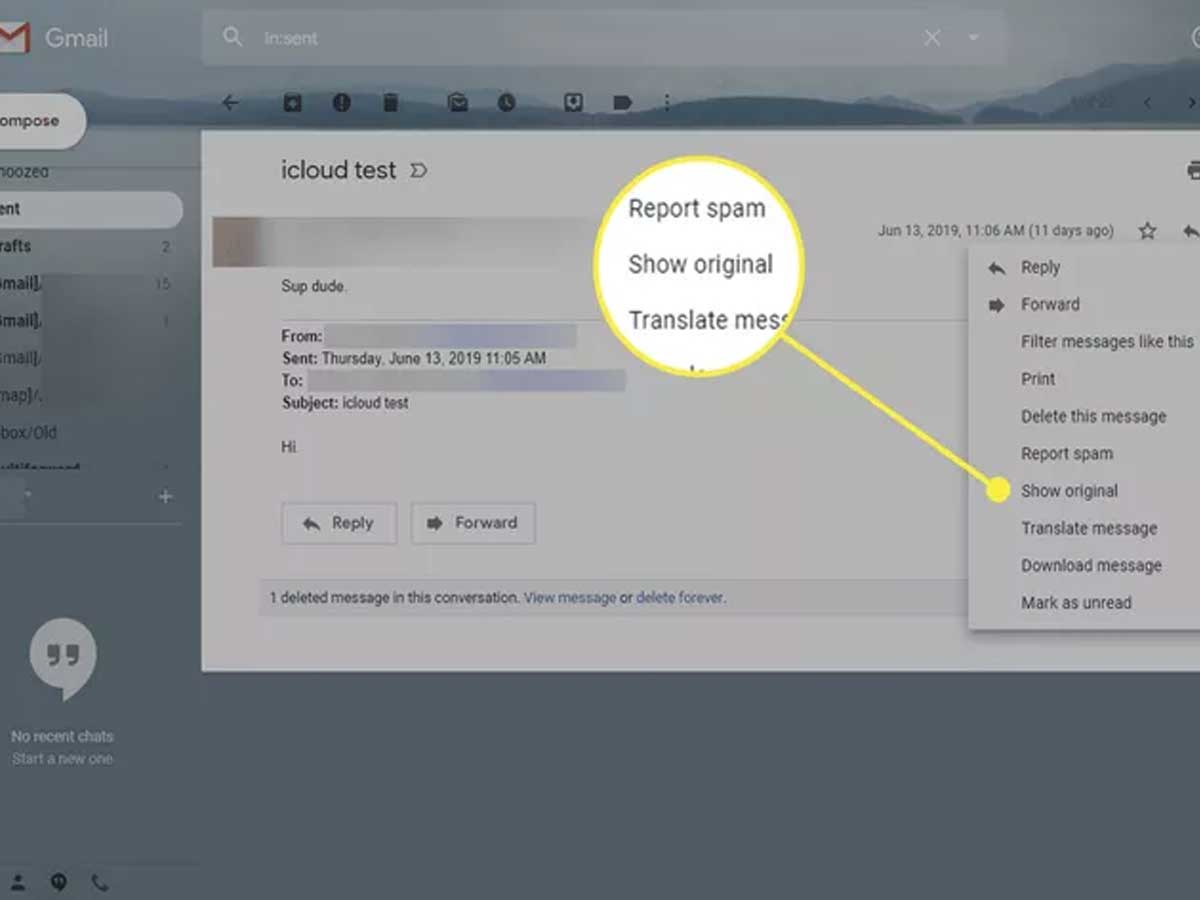
Email spoofing primarily revolves around manipulating email headers, which are responsible for providing essential information about the message's origin and path. In addition, cybercriminals forge sender addresses, making it appear as if the email is from a trusted source or a known individual. By exploiting this trust, they deceive recipients into believing that the message is legitimate and from a reliable sender.
The consequences of falling for spoofed emails can be severe. Users who unknowingly interact with these fraudulent messages may end up clicking on malicious links, unknowingly installing malware, or divulging sensitive information to unauthorized individuals. In addition, email spoofing techniques often aim to exploit human vulnerability and trust, making it crucial for individuals to stay vigilant and adopt proper security measures.
Design of Email Systems
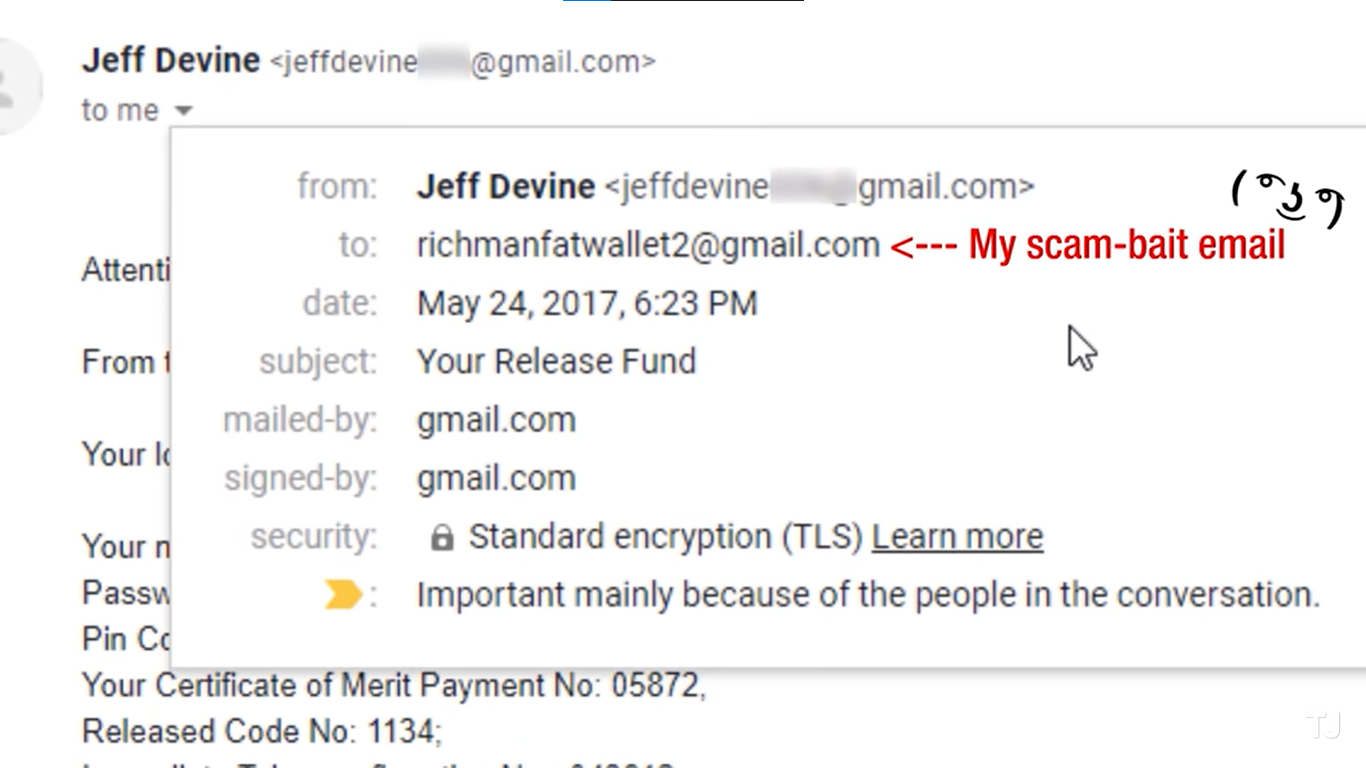
While convenient and widely used, email systems have inherent vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit. One of the key factors contributing to email spoofing is the sender's ability to assign their address without verification. This lack of verification allows malicious actors to impersonate legitimate senders and manipulate the recipients' perception of the email's authenticity.
Furthermore, not all email services have robust security protocols to detect and prevent spoofed messages. While some recipient servers and antimalware software can identify and filter out such emails, not all email systems benefit from these protective measures. This disparity in security protocols across different email services creates an environment where email spoofing can occur with varying difficulty levels.
Reviewing Email Headers
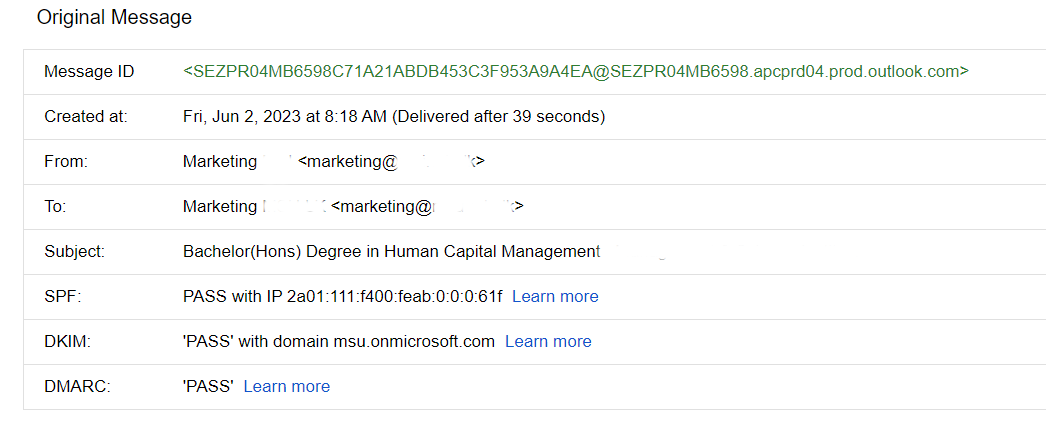
To mitigate the risks associated with email spoofing, reviewing and analyzing email headers for any signs of manipulation or deception is essential. In addition, examining email headers allows recipients to identify forged sender addresses and other suspicious elements that may indicate the presence of a spoofed email.
When reviewing email headers, individuals should pay close attention to the presence of security protocols such as SPF (Sender Policy Framework), DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance). These authentication technologies provide additional layers of verification and help establish the legitimacy of the email's source.
Email Authentication Protocols

In the ongoing battle against email spoofing, implementing robust email authentication protocols plays a vital role in bolstering security measures. These protocols help verify the authenticity of emails and ensure that they originate from legitimate sources. Explore the three key email authentication protocols: SPF, DKIM, and DMARC.
SPF (Sender Policy Framework)
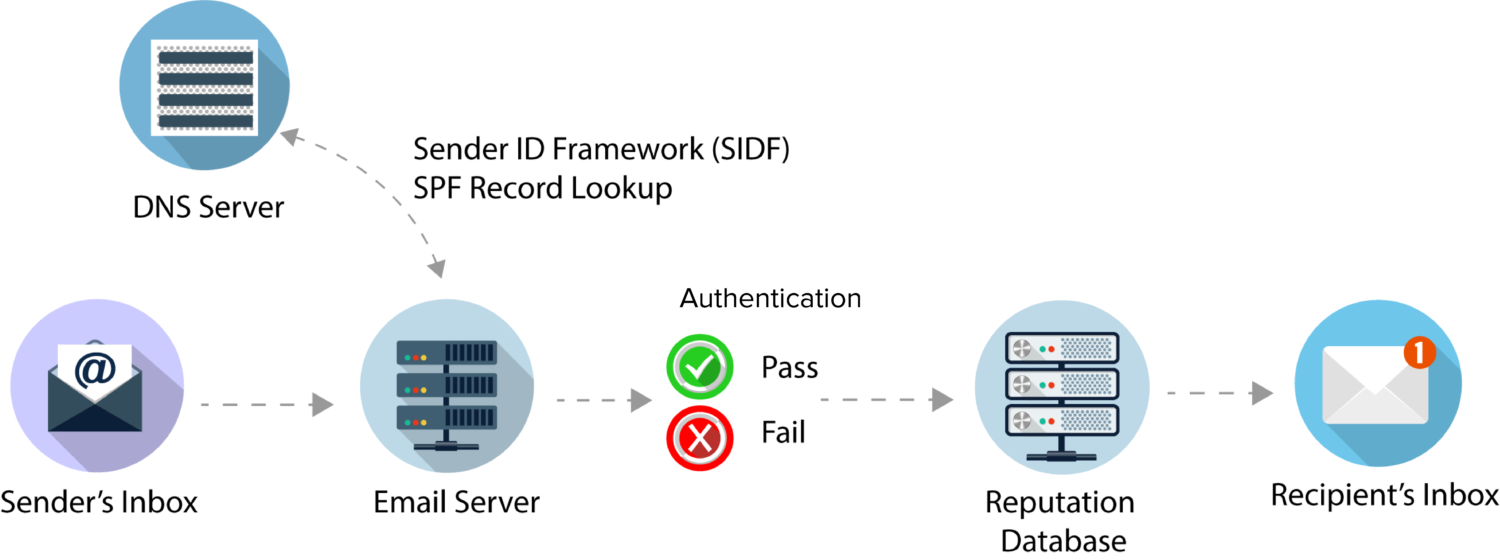
SPF, or Sender Policy Framework, is a widely used email authentication protocol designed to verify the authorization of the sending server. It helps prevent email spoofing by allowing domain owners to specify the authorized IP addresses or servers permitted to send emails on their behalf. When an email is received, the recipient's server checks the SPF records in the domain's DNS to confirm if the sending server is authorized. A pass or fail determination is made based on whether the sending server matches the authorized list.
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail)
DKIM, or DomainKeys Identified Mail, is another critical email authentication protocol focusing on message integrity and sender verification. DKIM uses encryption techniques to ensure that the content of the email remains intact and to verify the sender's authenticity. The sending server attaches a digital signature to the email using a private key, and the recipient's server decrypts and verifies this signature using the corresponding public key.
By comparing the encrypted hash of the message with the decrypted hash, DKIM confirms that the email has not been tampered with and originated from the claimed sender. It is important to note that DKIM serves a different purpose than SPF, and both protocols are essential for comprehensive email authentication.
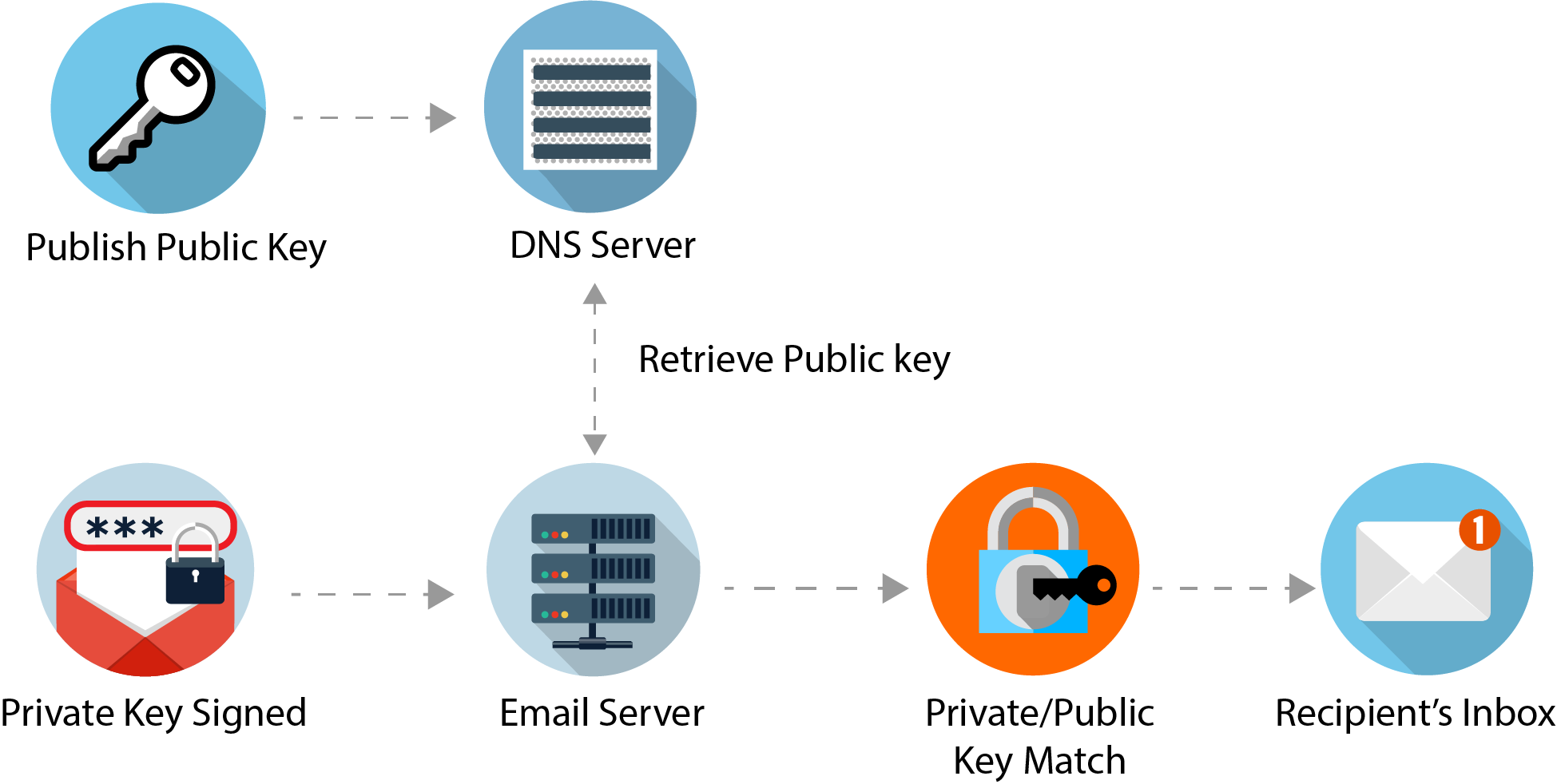
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance)
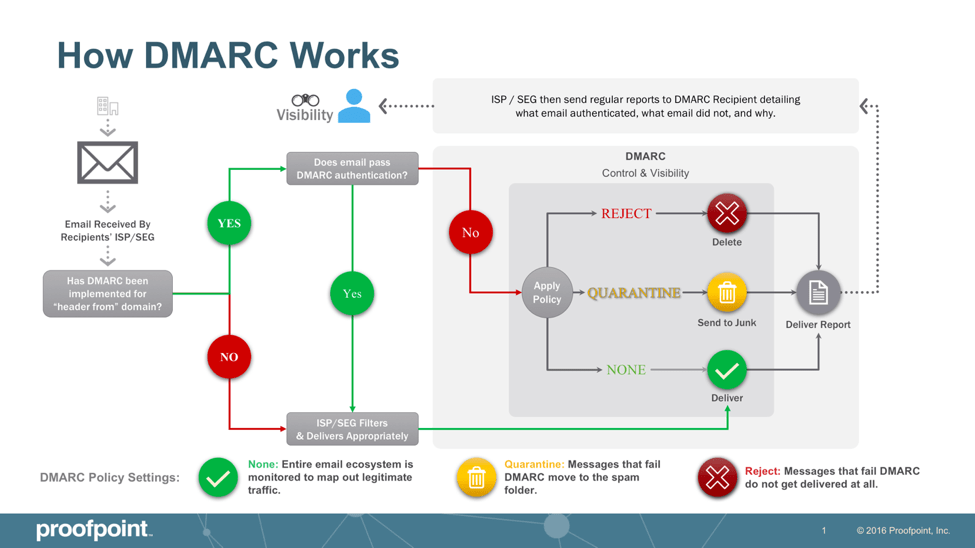
DMARC, or Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance is a powerful email authentication protocol that enhances security by verifying SPF and DKIM records for the displayed address. DMARC builds upon the strengths of SPF and DKIM to provide a more comprehensive authentication mechanism.
In addition, it allows domain owners to set policies for handling emails that fail authentication, from doing nothing to quarantining or outright rejecting them. At the same time, DMARC offers significant benefits in combating email spoofing, but its adoption and enforcement present challenges. Many domains still need proper DMARC records, and the lack of consistent enforcement policies reduces its overall effectiveness.
Best Practices to Avoid Email Spoofing
Deploying Email Security Measures
Deploying robust email security measures is crucial to bolster your defense against email spoofing. Email security gateways are vital in identifying and blocking suspicious emails before they reach your inbox. These gateways employ sophisticated algorithms and pattern recognition techniques to filter out fraudulent messages, reducing the risk of falling victim to email spoofing.
Additionally, utilizing reliable antimalware software can help detect and block emails containing malicious attachments or links that could compromise your system's security. Finally, implementing encryption techniques adds an extra layer of protection, safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access.

Utilizing Email Security Protocols
Utilizing email security protocols is essential in reducing the threat of email spoofing. The Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) and authentication protocols such as SPF, DKIM, and DMARC play a significant role in authenticating senders and preventing spoofed emails from reaching your inbox.
By configuring SPF records, domains can specify the authorized servers that can send emails on their behalf, reducing the chances of spoofing. DKIM ensures message integrity and sender verification through cryptographic keys, while DMARC adds a layer of authentication by aligning SPF and DKIM for the displayed address. Reverse IP lookups and DNS records also contribute to the authentication process, verifying the legitimacy of senders' identities.
Educating Users on Cyber Awareness

One of the most effective ways to combat email spoofing is by educating users about cyber awareness. Organizations can empower their workforce to be vigilant and proactive in identifying and reporting suspicious emails by training employees to recognize and handle spoofing attempts. This training should include real-life examples of email spoofing tactics and how to spot them.
It is crucial to continually update training materials to address emerging threats and stay current with the latest email spoofing techniques. By fostering a culture of cyber awareness, individuals can become the first line of defense against email spoofing attacks.
Exercising Caution and Vigilance

Individuals must exercise caution and vigilance when it comes to email communication. Checking the "From" and "Reply-To" domains for discrepancies is essential in identifying potential spoofed emails. Scrutinize the email address and domain, looking for any irregularities or slight variations indicating a spoofing attempt. Verify the origins of the email and compare them to your expectations.
Be wary of unsolicited emails, especially those requesting personal information or containing suspicious attachments or links. Only click links or open attachments if you know their legitimacy. Remember that reputable organizations typically do not ask for sensitive information via email. When in doubt, verifying the email's authenticity through a different means of communication, such as contacting the organization directly, is always safer.

Adopting best practices such as deploying email security measures, using security protocols, educating users, exercising caution, and remaining vigilant can dramatically lower the chance of email spoofing attacks for individuals and organizations. Being proactive means remaining up-to-date on emerging threats and evolving techniques in this space, and since email remains one of our primary communication modes, we must secure our inboxes against cybercriminals!
Remember, every email received is an opportunity for caution, verification, and protection of ourselves and our valuable information by adopting a proactive and informed approach to email spoofing detection and providing trustworthy communication experiences for all.
Sources: support.google.com / cloudflare.com / proofpoint.com / techtarget.com / crowdstrike.com /













