Google has rolled out its conversational AI chatbot, Bard, to users in the European Union (EU) and Brazil after months of preparation and regulatory discussions. Bard now supports over 40 languages and comes equipped with new privacy features that give users more control over their data.
However, EU regulations aimed at protecting user privacy have slowed the release of new products like Bard. As chatbots based on large language models continue to spread globally, Google emphasizes the importance of transparency and open communication with regulators around privacy.
One of the notable improvements in Bard is its expanded linguistic knowledge. Users can now converse with Bard in nearly four dozen languages, including Arabic, Chinese, German, Hindi, Spanish, and more.

What languages Bard AI support?
- Afrikaans
- Arabic
- Bengali
- Bulgarian
- Chinese (Simplified)
- Chinese (Traditional)
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- French
- German
- Greek
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Indonesian
- Italian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Norwegian
- Polish
- Portuguese (Brazil)
- Portuguese (Portugal)
- Romanian
- Russian
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Spanish
- Swedish
- Thai
- Turkish
- Ukrainian
- Vietnamese
This significant expansion allows users from various regions to communicate effortlessly with the chatbot AI. Google has taken into account user feedback and adhered to its AI Principles, ensuring that Bard's expansion into new languages and regions is guided by privacy and data protection measures.
With the latest updates, Bard provides users with a unique choice when interacting with the chatbot AI. Users can now opt to either read or listen to Bard's generated responses.
This feature proves especially beneficial when users want to hear the correct pronunciation of words in the 40 newly-added languages. By accommodating different learning preferences, Bard offers a more inclusive and accessible conversational experience.
Another exciting aspect of Bard's update is the increased control users have over its tone. Users can now select from five distinct options for Bard's tone: simple, long, short, professional, or casual.
Although these robust tone controls are currently available only for English-language requests, Google is actively working to expand them to the other languages supported by Bard. This level of customization allows users to personalize their interactions with Bard, making the experience more tailored and engaging.
Bard has also acquired the ability to interpret images dropped into the chat. This feature enables users to prompt Bard with an image and receive information or generate captions based on its content.
The image interpretation capability adds a new dimension to the chatbot AI's functionalities, making it faster and easier for users to extract relevant information or generate contextually appropriate captions. It's worth noting that this feature is currently available only in English.
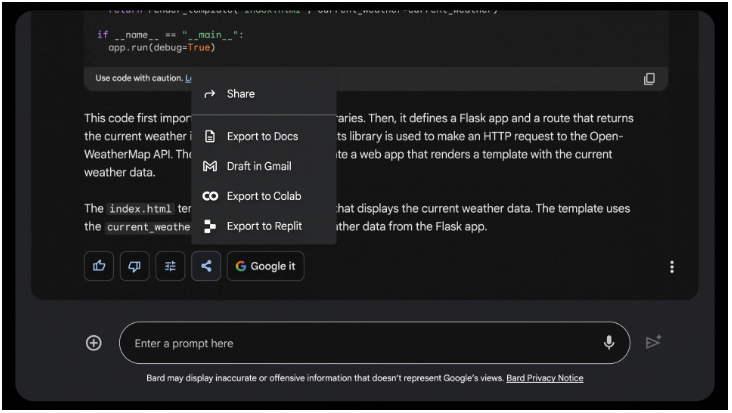
Collaboration and organization are essential aspects of any chatbot AI, and Bard has made notable strides in these areas. Users can now export Bard-generated Python code to Replit and Colab, two popular platforms for code collaboration.
This improvement simplifies the process of sharing code with collaborators, enhancing workflow efficiency. Additionally, users can copy and share portions of individual chats with others, allowing for more seamless knowledge transfer and communication.
Furthermore, Bard introduces pinned conversations, a feature that enables users to organize and revisit important or frequently referenced discussions. Pinned conversations act as bookmarks, facilitating quick access to relevant information whenever needed. Additionally, users can rename conversations, further aiding in the organization of their interactions with Bard.

Google's Bard chatbot AI has recently been made available to users in the European Union and Brazil, marking an expansion of its user base to these regions. However, the EU rollout of Bard faced a slight delay due to compliance concerns regarding the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
To address these concerns, Google engaged in productive conversations with privacy regulators in Europe, ensuring that Bard aligns with the necessary privacy standards. Consequently, users can expect clear notices and control options that govern the usage and storage of their data, not only in the EU but globally as well.
The challenges related to data protection and AI chatbots are not unique to Bard. OpenAI's ChatGPT, for instance, faced a temporary shutdown in Italy due to similar data protection issues.
As the development and deployment of advanced AI technologies continue, compliance with evolving data protection laws becomes increasingly critical. Tech companies like Google and Meta Platforms Inc. must navigate these regulatory landscapes to ensure the successful rollout of their innovative chatbot solutions.
Google has plans to further enhance Bard with additional features. One notable upcoming addition is the ability to hear spoken responses from Bard, expanding the range of communication options even further. Users will have the choice to listen to the chatbot AI's responses, providing an immersive and dynamic conversational experience.
Additionally, Google aims to enable users to upload images to prompt Bard and receive information or analysis based on the visual content. This enhancement will build upon Bard's existing image interpretation capabilities, empowering users to explore a broader range of conversational possibilities.
Sources: engadget.com / bloomberg.com / blog.google













