In the shadows of the Industrial Revolution, a group of British textile artisans emerged as unlikely heroes, standing steadfast against the relentless march of machinery. Their actions sparked controversy, ignited debates, and left an indelible mark on history. But don't worry; we're not here to discuss a battle of Terminator proportions—no machines rising against humanity. At least not yet.
Instead, we delve into the fascinating world of the Luddites, where skilled weavers transformed into rebels, and the clash between tradition and technology reached its crescendo. So, take out your tin foil hats, sit comfortably, and fasten your seatbelt in your time machine. We're about to embark on a captivating journey back to the 19th century, where the secrets of the Luddites await.
The Luddite Movement in the 19th Century
The Luddite Movement of the 19th century arose as a direct response to the rapid mechanization that swept through the British textile industry during that time. The movement was primarily fueled by skilled machine operators, including weavers and textile workers, who were genuinely concerned about the consequences of machinery on their livelihoods and the overall socio-economic landscape.
The primary fear driving the Luddites was the imminent threat of unemployment, which would have dire consequences, pushing them into poverty. Additionally, they perceived the introduction of machinery as a direct challenge to their craftsmanship and expertise. The artisans firmly believed that the rise of unskilled machine operators would replace their roles, leading to a decline in textile quality and a subsequent reduction in wages.
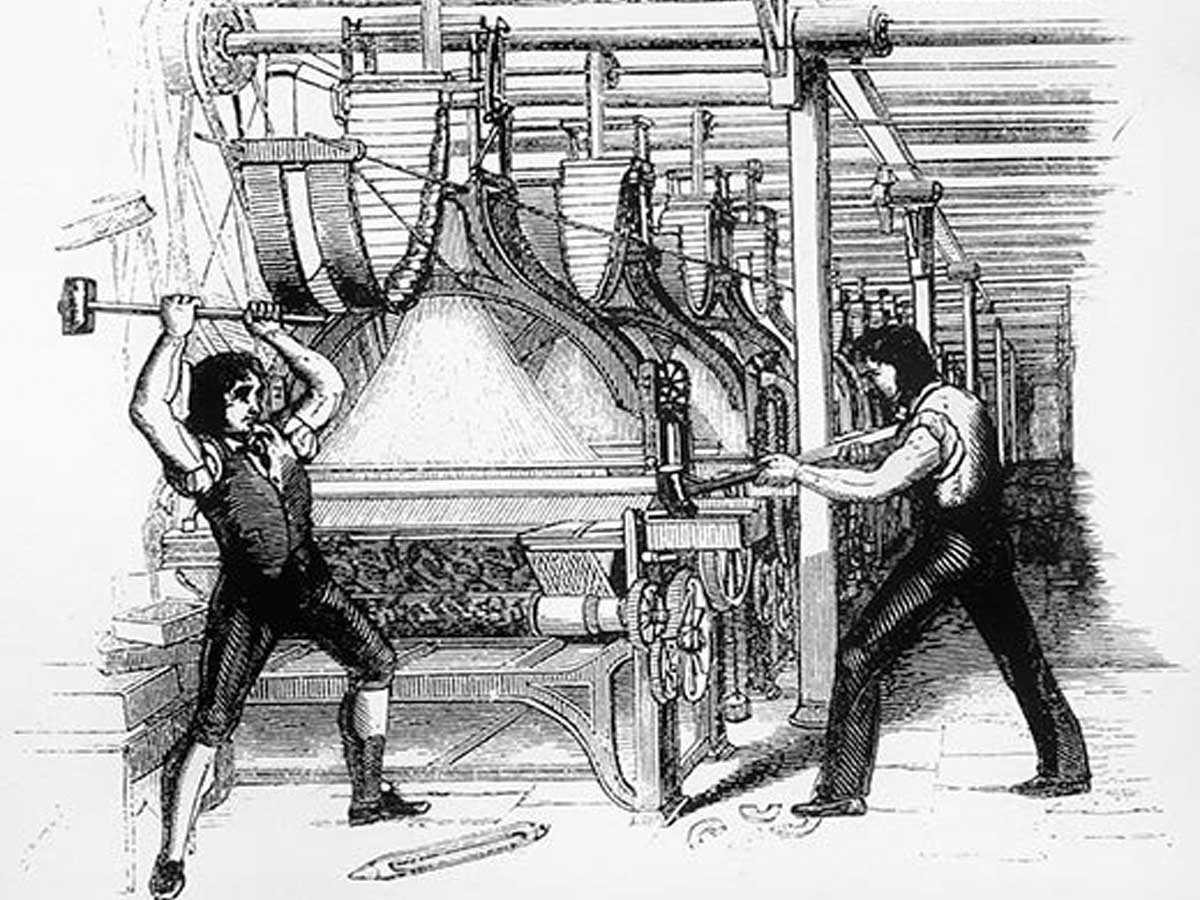
Motivated by their grievances, the Luddites formed tightly-knit groups in manufacturing towns and cities. United by a common cause, these communities aimed to resist the intrusion of machines into their trade. Their collective efforts were focused on protecting their livelihoods and preserving the long-standing labor practices of their profession.
To impede the progress of mechanization, the Luddites resorted to sabotage and machine destruction. Their targets were factories where machines were employed to bypass established labor practices. By dismantling and rendering the machines inoperable, they protested tangibly, displaying unwavering resistance to the perceived threat.

The British government implemented stringent measures in response to the growing unrest and the destructive impact of Luddite activities. They enacted laws and regulations to suppress the movement and safeguard the interests of industrialists.
One of the harshest measures introduced was capital punishment for individuals found guilty of machine-breaking, serving as an explicit deterrent to discourage further acts of sabotage.
The strict actions taken by the British government reflected the deep concerns and anxieties sparked by the Luddite movement. Authorities were driven by the desire to maintain the progress of industrialization and ensure stability in the emerging factory-based economy.
Through the imposition of severe penalties, including the threat of death, they aimed to suppress the Luddite movement and discourage others from joining their cause.
Impact and Legacy of the Luddite Movement
Questions Raised about Technology and Employment

The Luddite movement of the 19th century left a lasting impact that continues to resonate in contemporary discussions surrounding technology and employment. The actions of the Luddites raised critical questions about the consequences of technological advancements on the labor market and the broader social fabric.
The Luddites' resistance to introducing machinery stemmed from their deep concerns about the potential loss of jobs and the displacement of skilled workers. Their fears centered on the belief that the rapid mechanization of industries would render their craftsmanship obsolete and lead to widespread unemployment.
These concerns prompted a reflection on the balance between technological progress and the well-being of workers, with many questioning whether the benefits of innovation would come at the expense of human livelihoods.
Modern Usage of the Term "Luddite"

The term "Luddite" has transcended its historical roots and found a place in modern discourse. Today, it is often used to describe individuals or groups who display skepticism or resistance toward new technologies. The term symbolizes a cautious or critical stance toward the rapid pace of technological advancements and the potential societal implications they carry.
While not all labeled as Luddites share the same motivations as their 19th-century counterparts, the term has evolved to encompass a broader sentiment of concern or resistance to change. In popular usage, it captures the tension between embracing progress and safeguarding the interests of workers, as well as the ongoing debate about the impact of technology on various aspects of our lives.
Employing Technology to Oppose New Technologies
Ironically, in today's world, there are instances where technology itself is employed to resist or challenge the introduction of new technologies. This paradoxical approach is reminiscent of the Luddite movement, albeit with a different context and purpose.
Groups and individuals concerned about the potential adverse effects of certain technologies have leveraged the power of digital platforms and social media to voice their dissent and mobilize support.
Online campaigns, petitions, and grassroots movements have emerged to raise awareness, advocate for ethical practices, and encourage responsible innovation. This utilization of technology to oppose the negative consequences of technology represents a modern twist on the Luddite legacy.
The Luddite Protests and Symbolism
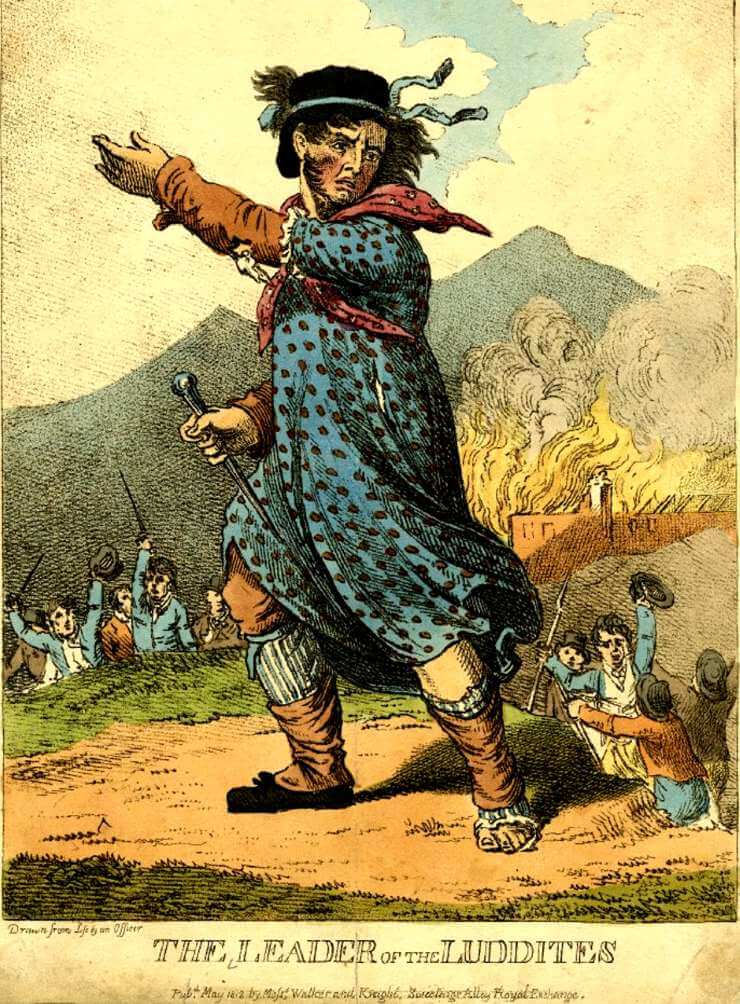

The Luddite protests centered around the stocking frame, a mechanical knitting machine used in the textile industry. This particular machine became the embodiment of the Luddites' grievances and the symbol of their resistance. They saw the stocking frame as a representation of the threat posed by machinery to their livelihoods and craftsmanship.
There were misconceptions surrounding the organization and the perceived danger of the Luddite movement. While the Luddites were indeed organized into groups, their activities were not as coordinated or threatening as some portrayals suggest. The protests were localized, with groups acting independently in different manufacturing towns and cities. The scale of the destruction caused by the Luddites was limited, and they mainly targeted specific machines that they believed bypassed established labor practices.

The Luddites gained notoriety and recognition through the fictional character Ned Ludd. According to legend, Ned Ludd was an apprentice who destroyed a knitting machine in a fit of rage. His name became synonymous with the movement, and "Luddite" was used to describe those opposed to technological advancements.
Although the character of Ned Ludd was fictional, it added a compelling narrative to the Luddite protests and further heightened public interest in their cause.
The Luddite protests had a unique blend of seriousness, humor, and mockery. While their concerns about the impact of machinery on their livelihoods were genuine, there was also an element of wit and satire in their actions.
For example, the Luddites often left behind handwritten notes, mockingly attributing their deeds to Ned Ludd himself. These notes and the destruction of machinery served as a form of protest that combined serious resistance with a touch of fun.
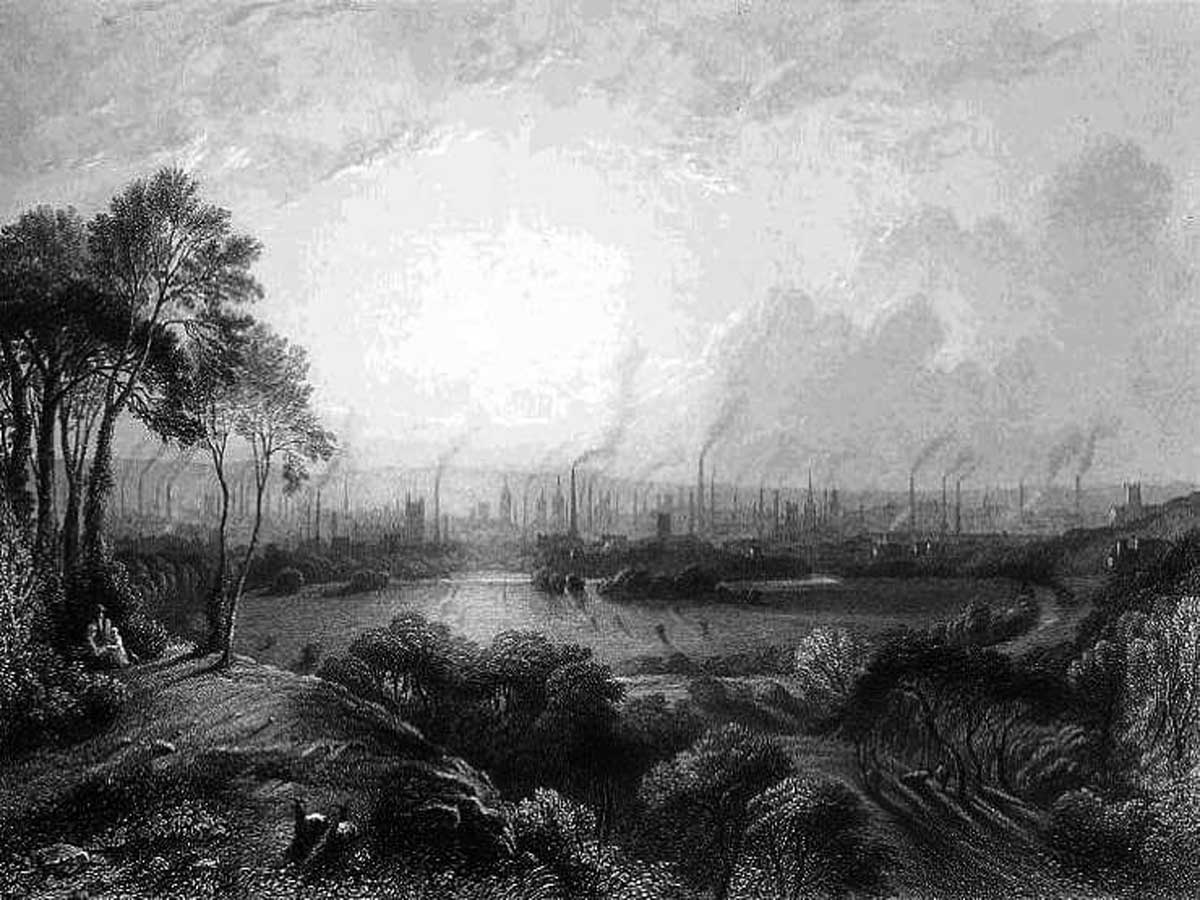

The Luddite protests and their symbolism revolved around the stocking frame, misconceptions about organization and danger, the fictional character Ned Ludd, and the mixture of seriousness, humor, and mockery. The stocking frame represented the perceived threat of machinery to the artisans' craftsmanship and livelihoods.
Despite misconceptions about their organization, the Luddites operated locally and targeted specific machines. The character of Ned Ludd added notoriety to the movement, while the Luddites' actions blended seriousness and humor through handwritten notes and mock attributions. This combination of elements contributed to the unique nature of the Luddite protests and the symbolism they created.
The Influence of Technology and the Necessity of Finding Equilibrium
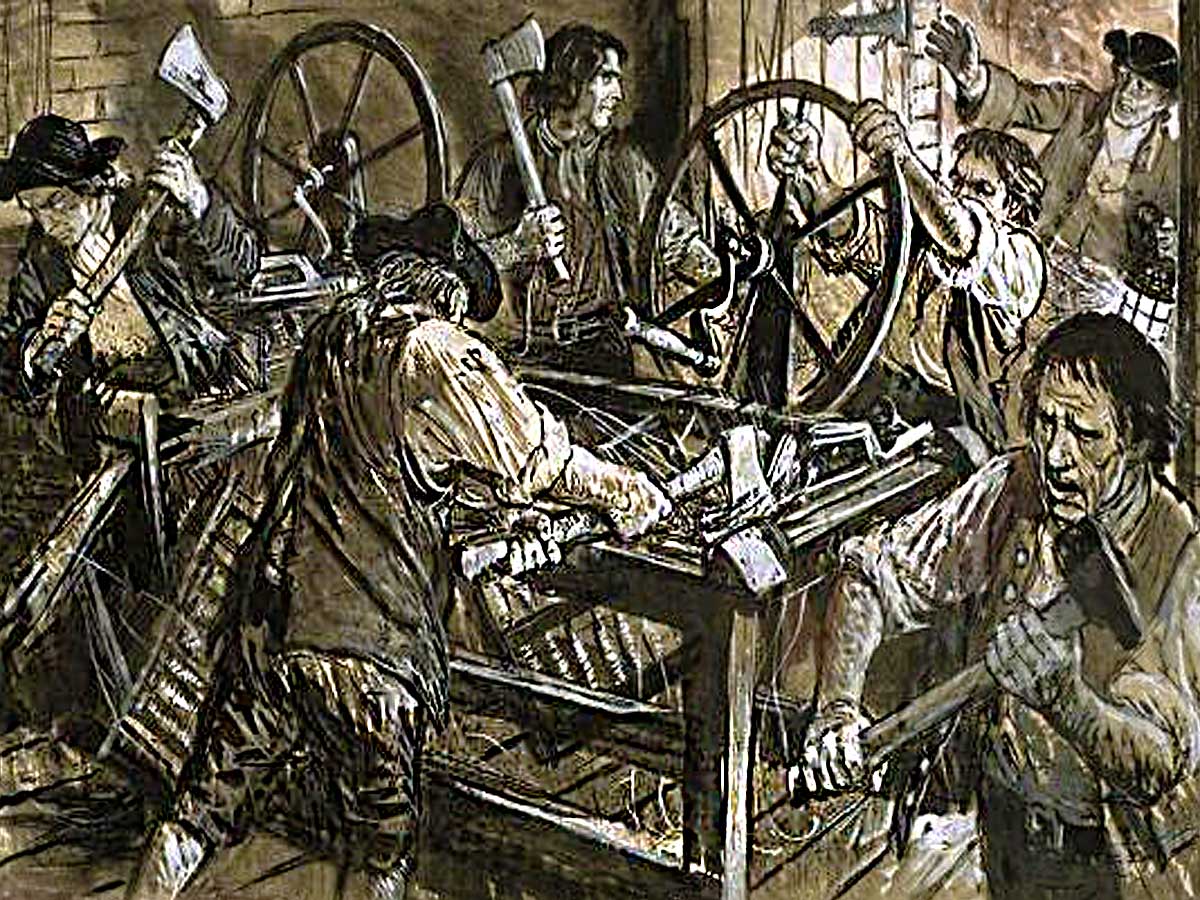

The advent of the Industrial Revolution in history brought forth a wave of advancements that left an indelible mark on society. The far-reaching consequences of this period yielded a plethora of benefits, including heightened productivity, improved living standards, and the birth of new industries. Nevertheless, as with any significant change, there were both positive and negative ramifications to consider.
The mechanization of various sectors resulted in job displacement and the erosion of traditional skills. Furthermore, the conditions prevalent in factories during this era often featured long working hours and minimal safety regulations. These dynamics have spurred a critical reflection on the need to strike a delicate balance between progress and the well-being of individuals and communities.
A Personal Reflection on the Luddite Legacy: Embracing the Human Spirit in the Age of AI

As we delve into the concerns voiced by the Luddite movement of the past, we find ourselves at a pivotal moment where history appears to echo its warnings. The advent of artificial intelligence (AI) has revived anxieties about job displacement and the potential domination of machines in the workforce. So let us briefly pause to contemplate: were the Luddites perceptive in their apprehensions? Have their fears materialized over time?
Undoubtedly, there are remarkable parallels between the Luddites' trepidations regarding technology and the general uneasiness surrounding AI today. Just as the Luddites harbored concerns about losing their means of livelihood to automated machines, many individuals today harbor similar worries about the implications of AI for their professional prospects.
These concerns are not baseless, for despite the remarkable strides made in AI, distinctive human qualities still elude its grasp.

Now, as we find ourselves on the verge of a future shaped by the ever-expanding realm of AI, let us wholeheartedly embrace it with a mindset oriented toward growth and adaptability. Rather than surrendering to fear, let us channel our energy into upskilling ourselves, staying abreast of the latest developments, and nurturing an innovative spirit.
In doing so, we position ourselves as invaluable assets in a world where the human touch, emotional intelligence, and creative aptitude cannot be effortlessly replicated.
You see, my friends, the legacy of the Luddites serves as a timeless reminder of the perpetual struggle to strike a delicate balance between progress and preserving our inherent humanity. In times of change and uncertainty, we have the opportunity to rise above our fears and limitations, harness our uniquely human qualities and push the boundaries of what is possible.
Let us draw wisdom from their cautionary tale as we forge ahead with resilience, embracing AI not as a threat but as a catalyst for innovation and growth.
The path ahead may seem daunting, but within every one of us lies the capacity to evolve, learn, and adapt. We are not mere bystanders in this technological revolution but the architects of our destiny.
So, let us step into the future with unwavering determination, knowing that our ability to embrace change, nurture our human connections, and infuse our work with creativity will ensure our enduring significance in an ever-evolving global landscape.
Embrace the possibilities, my friends, for the age of AI is not a twilight of humanity but a dawn of new opportunities. Together, we can shape a future where the harmony between technology and our human essence illuminates the path toward progress and prosperity.
So let us march forward with optimism, inspiring one another to unleash our full potential and create a world where the symphony of human ingenuity and AI harmoniously intertwines.
We should thrive based on our limitless capabilities rather than fear of being replaced. Like the Luddites, we should question and strive for progress. Let's work together towards a bright future where our humanity is more evident.
Sources: smithsonianmag.com / history.com / historic-uk.com / nationalarchives.gov.uk / britannica.com / digitalcommons.nyls.edu












