Step into the captivating realm of search engine algorithms, where the convergence of information and technology opens up endless possibilities. With each passing year, these ingenious tools reshape our online exploration, enabling us to effortlessly navigate the vast expanse of the internet in search of answers.
From the early stages when human curation was the norm to the sophisticated algorithms powering today's search engines, the evolution has been nothing short of extraordinary.

The Early Days of Search Engines
In the early days of search engines, the task of maintaining and updating them fell on the shoulders of human beings. This manual approach, though meticulous, came with its limitations. It was a labor-intensive and time-consuming process that made search engines expensive to operate, frustratingly slow, and restricted in their ability to index websites comprehensively.
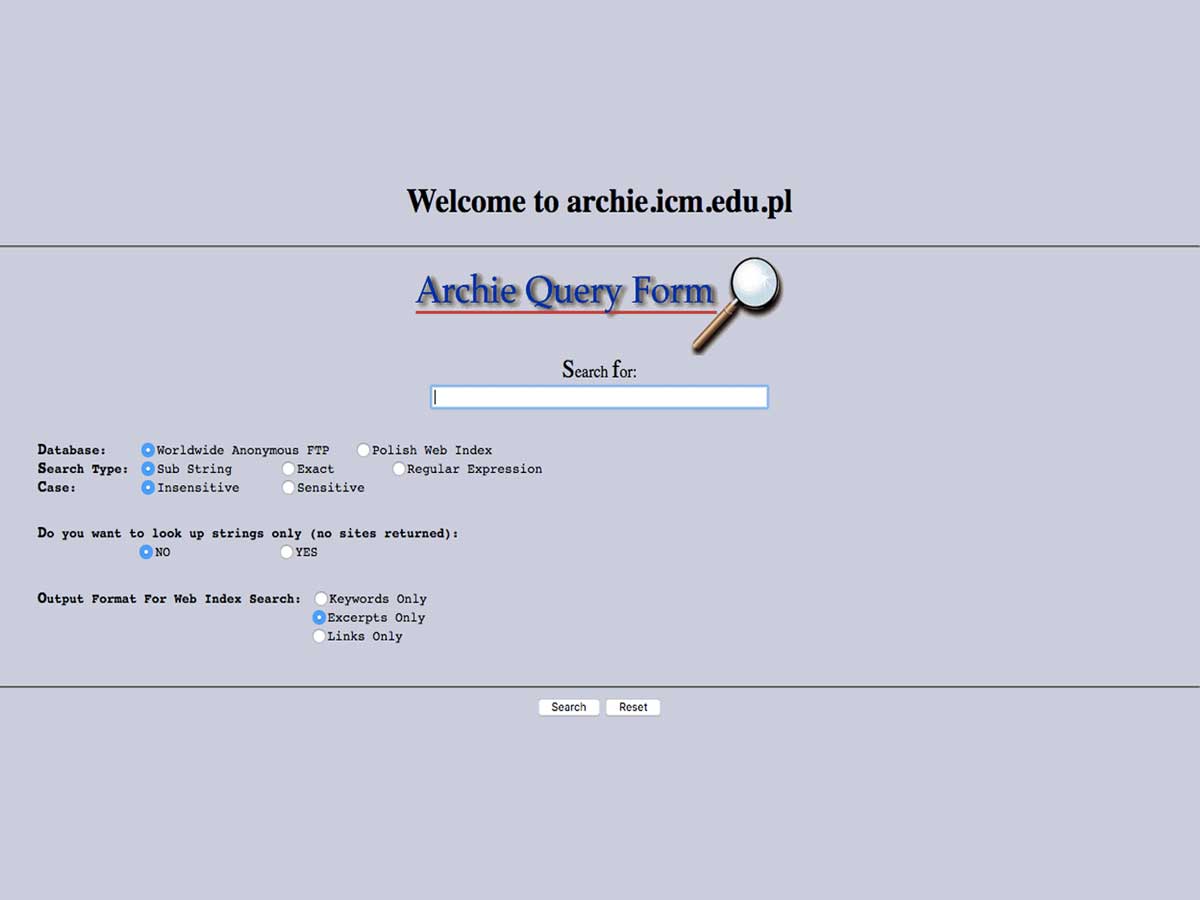
The pioneering search engine, "Archie," emerged in 1990, initially designed to index FTP sites. Around the same time, Architext introduced a groundbreaking concept by incorporating statistical analysis of word relationships into the search process. These advancements laid the foundation for future developments in search engine algorithms.
Matthew Gray's World Wide Web Wanderer and Martin Koster's ALIWEB played vital roles in advancing web indexing and site submission techniques. These early contributors expanded the scope of search engines by enabling them to explore and catalog a wider array of web content.
However, early bot-fed search engines such as JumpStation, World Wide Web Worm, and RBSE Spider faced significant challenges in terms of indexing and relevance. Their capabilities were limited, hindering their ability to provide users with accurate and comprehensive search results.

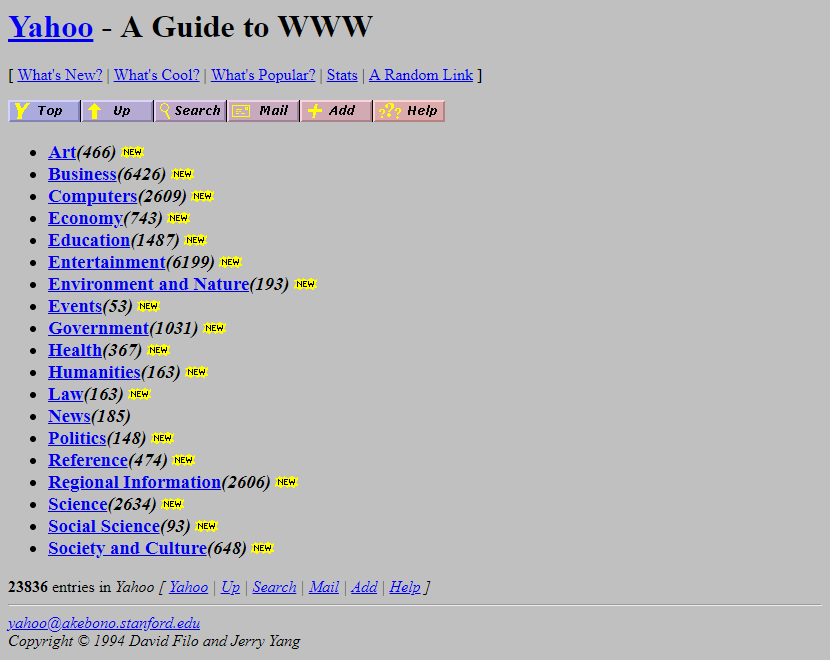
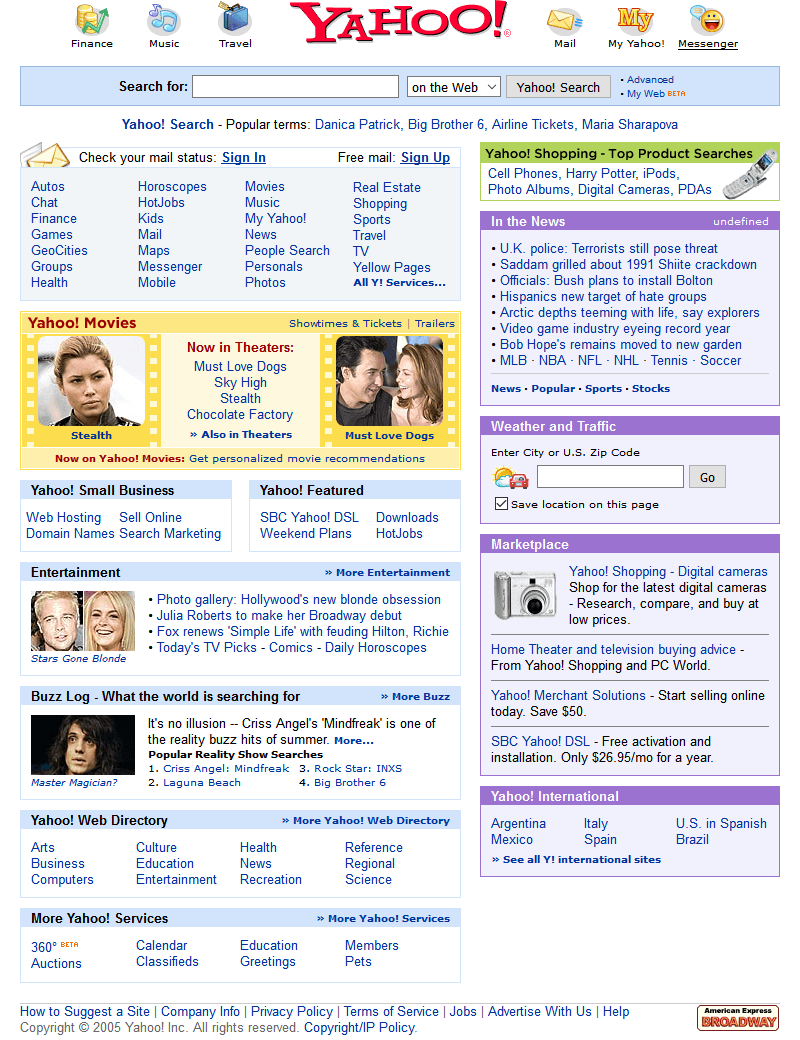
The Rise of Yahoo!
In 1994, Yahoo! burst onto the scene, initially serving as a curated directory of favorite websites. Over time, it evolved into a prominent corporation, celebrating its 25th anniversary in 2020. While Yahoo! began as a directory, its influence and impact on the search engine landscape cannot be understated.
During this period, significant advancements were made in the indexing capabilities of search engines. WebCrawler, introduced in 1994, became the first crawler to index entire web pages, revolutionizing the way information was retrieved from the web. Another player in the field, Lycos, gained popularity due to its impressive index size, providing users with a vast array of search results to explore.
Additionally, Infoseek emerged as a notable search engine, offering users the ability to submit their websites for inclusion in the search results. Meanwhile, AltaVista took search capabilities to new heights by providing advanced techniques and search tips, empowering users to refine their queries and obtain more precise results.
Inktomi's Hotbot search engine and Ask Jeeves, with its innovative natural language search functionality, also made their mark during this period of search engine development, offering users alternative approaches to accessing information online.
The Emergence of Google
The emergence of Google signaled a significant turning point in the evolution of search engines. Initially known as BackRub, Google introduced novel concepts that would reshape the landscape of online search. Teoma, another player in the field, brought clustering techniques to the forefront, enhancing the organization and presentation of search results.
Google's breakthrough came in the form of its PageRank algorithm, which leveraged link analysis and citation notation to determine the relevance and importance of web pages. This innovative approach to ranking web content set Google apart from its competitors and laid the foundation for its mission to organize and make information accessible and useful to users.

Driven by a commitment to continual improvement, Google constantly enhances its algorithms to provide the most accurate and relevant search results. Their focus lies in presenting users with the best document links, placing a premium on precision and relevance in order to meet the ever-increasing demands of users seeking valuable information.
How do Search Engines Work?
Understanding how search engines operate is essential to unraveling the magic behind their ability to deliver relevant results. A web search engine comprises three key components: robots (also known as crawlers), an index, and a user-friendly search interface.

Firstly, crawlers are the workhorses of search engines. They tirelessly explore the web, visiting websites and recording information from their pages. Then, by analyzing the content, links, and other factors, crawlers gather data to build a comprehensive index, which serves as a digital library of the web.
Once the index is established, users interact with the search engine through its search interface. This is where the magic happens. Users input their search queries, consisting of keywords or phrases, and the search engine's relevancy software kicks into gear. It sifts through the vast index to find the most relevant web pages that match the query and presents them to the user in a ranked order.
The ranking of search results is determined by complex algorithms employed by search engines. These algorithms consider various factors to determine the relevance and importance of a web page. Elements like the number of referrals from other websites, the authority of the page, and its status as a hub in the network all influence its ranking.

This ranking process brings us to the fascinating world of Search Engine Optimization (SEO). Website owners and creators employ SEO techniques to improve their site's visibility and ranking in search engine results. SEO methods can be classified as white hat (recommended), gray hat, or black hat based on their impact on search engine accuracy and user experience.
White hat SEO methods involve legitimate practices such as strategically placing important keywords in metadata, updating website content regularly, and cross-linking to increase authority. These techniques align with search engine guidelines and are considered ethical and beneficial for both users and search engines.
On the other hand, black hat SEO tactics are frowned upon and can lead to penalties from search engines. These unethical practices abuse the logic of search engines and include tactics like keyword stuffing, hidden text, and spammy link schemes. Search engines continually improve their algorithms to identify and penalize such practices, as they undermine the integrity of search results.
Search Engine Tasks Unveiled
In their quest to connect users with the most relevant and valuable information, search engines carry out three essential tasks: crawling, indexing, and ranking. Each task plays a pivotal role in the intricate web of search engine operations, ensuring that users receive accurate and tailored search results.
Crawling serves as the initial step in search engine operations, as it involves the exploration of the vast digital landscape. To accomplish this task, specialized software known as crawlers, spiders, or bots venture across the internet, diligently following links from one webpage to another. They tirelessly scour the web, constantly on the lookout for fresh content. Through their systematic visits and data collection, these digital explorers lay the foundation upon which the search engine's index is built.
Indexing takes center stage once the crawlers have amassed a wealth of information from web pages. This process kicks off as search engines meticulously organize and compile an extensive catalog of web pages and their respective content. This comprehensive index serves as a virtual library, enabling search engines to swiftly retrieve relevant results whenever users enter their queries.
The final critical task performed by search engines is ranking. When users submit their search queries, the search engine's ranking algorithms spring into action. These sophisticated algorithms meticulously scrutinize numerous factors to determine the order in which search results are presented to users. Elements such as keyword relevance, the quality and quantity of backlinks pointing to a webpage, and the freshness of the content all come into play during the ranking process. By meticulously considering these factors, search engines strive to provide users with the most precise and valuable results possible.
Explore The Importance of Search Engines and SEO

Search engines play an integral part in our online experiences today, offering us relevant and valuable information at the click of a button. These powerful tools have revolutionized how we access and navigate the vast expanse of the internet; with just a few keystrokes, we can tap into a world of knowledge that's readily accessible from various devices and locations.
Before the rise of search engines like Google, finding specific information online was an arduous and frustrating endeavor that involved manually exploring endless web pages in hopes of discovering what you were seeking - often leading to time wasted and unsuccessful results. Everything changed when search engines came along.
Alan Emtage stands as a pioneer in search engines, as the creator of Archie. Archie revolutionized information retrieval; users could now enter keywords or queries, and Archie would quickly search its database to return relevant results - marking a paradigm shift in information access and consumption, ushering us into an age of instant and efficient knowledge retrieval.
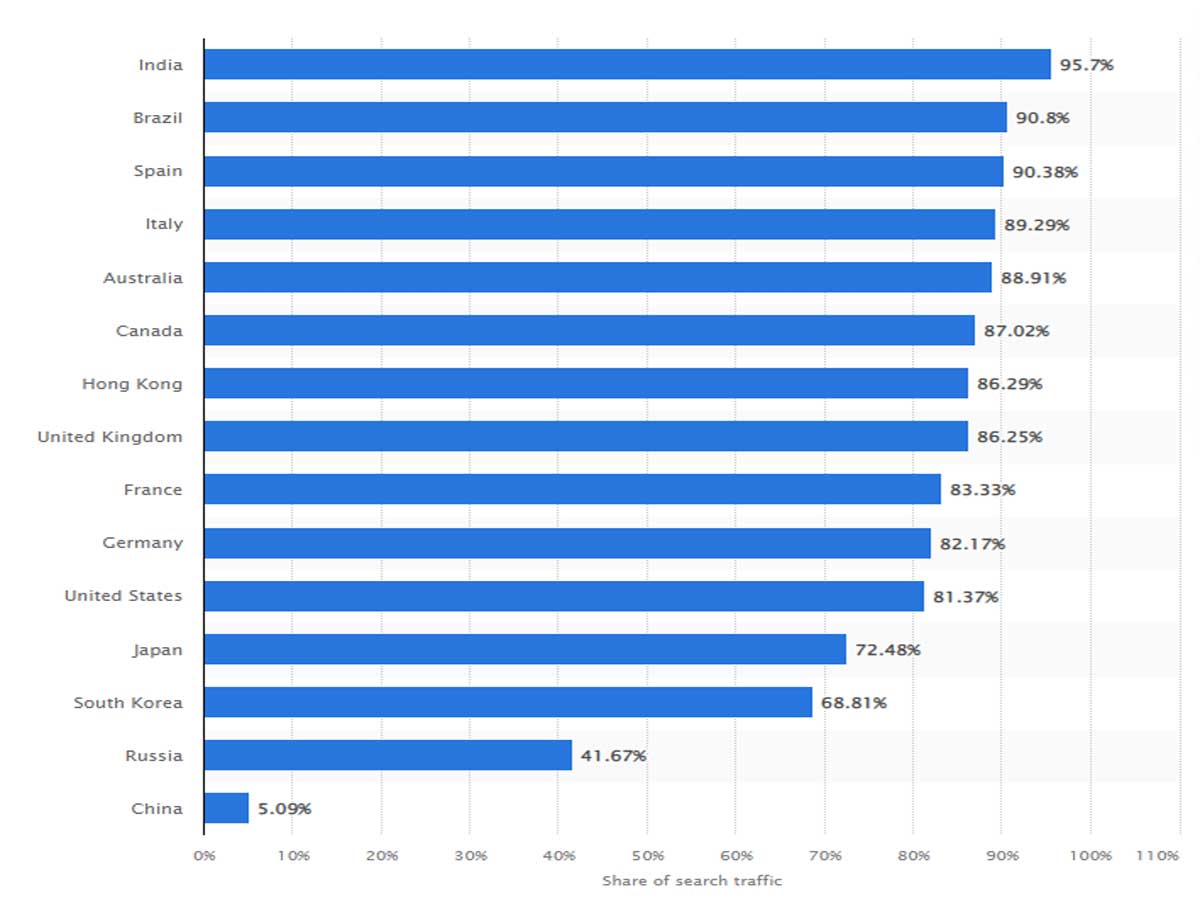
Search engines' impact and significance are underscored by the rapidly rising global Internet users. By January 2023, 5.06 billion individuals had active internet accounts worldwide, relying on search engines as a primary way of finding the information they needed - whether researching topics, seeking products/services, or keeping abreast with news updates. Search engines have become an integral part of daily life, and search engines continue to make headlines worldwide.
At the core of search engines' functionality lie complex ranking algorithms that use complex evaluation and evaluation processes to rank search results based on various factors such as referrals, authorities, hubs, and referrals - contributing factors including referrals, authorities, and hubs, among many others. Website owners and digital marketers recognize the significance of optimizing their online presence to increase visibility and rankings in search results; this practice is known as Search Engine Optimization (SEO).
White hat SEO techniques can be broken down into different approaches based on their impact on search engine accuracy and user experience. White hat techniques, which are recommended and ethical, including optimizing metadata by including important keywords, regularly updating website content, cross-linking to increase authority, and cross-linking as a means to gain more search engine authority. These strategies follow search engine guidelines with the aim of providing useful and valuable content that meets user demands.
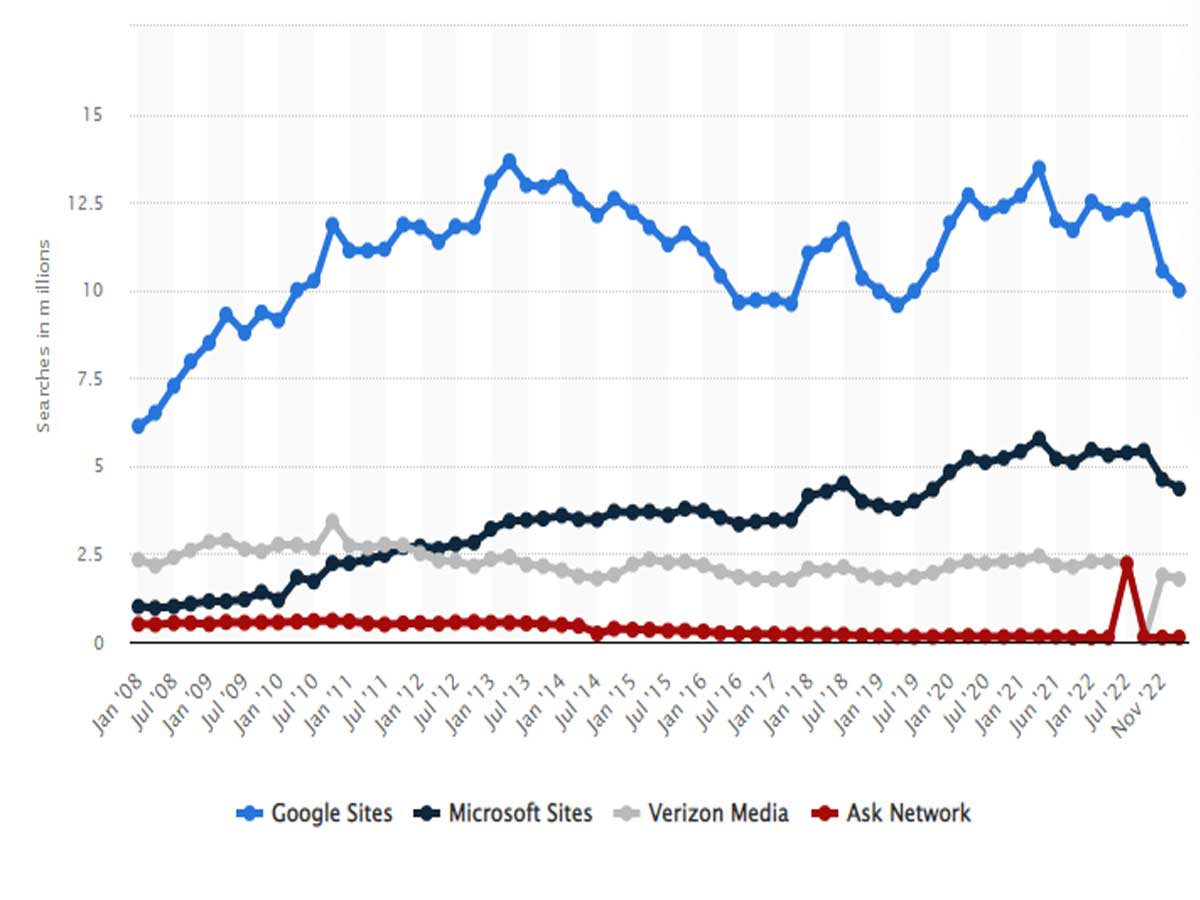
However, it should be remembered that search engines punish black-hat SEO tactics. Such techniques involve manipulating search engine logic and abusing its system for an unfair advantage - one common example being keyword stuffing, where excess and irrelevant keywords are unnaturally added into websites without their natural placement - practices such as this undermine search results while impairing user experiences.
As we gaze into the horizon, it's evident that search engines will keep progressing, driven by remarkable advancements in machine learning and artificial intelligence. These groundbreaking technologies will empower search engines to delve deeper into the essence of words, interpret queries within their contextual frameworks, and provide search results that are even more precise and tailored to individual users.
So, as you embark on your search endeavors, armed with the insights and understanding gained from this exploration, embrace the future of search engines. Adapt, innovate, and navigate this dynamic landscape with confidence and enthusiasm. Happy searching, and may your quest for knowledge and success be met with bountiful rewards!
Sources: topofthelist.net / captechu.edu / bdc.ca / graphics.stanford.edu / britannica.com / researchgate.net / khanacademy.org / bdc.ca / bbc.co.uk