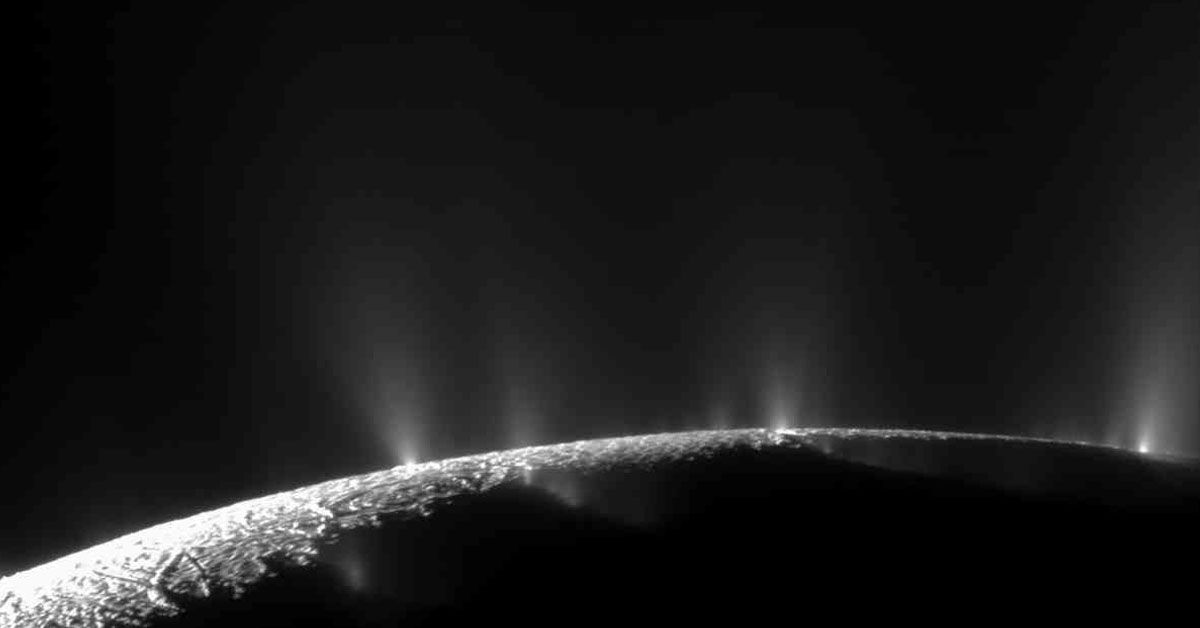
In a dramatic revelation that could reshape our wisdom of the universe, the James Webb Space Telescope has unveiled a colossal geyser on Saturn's moon, Enceladus. This icy moon, smaller than Arizona, has long intrigued scientists with its mysterious geysers. But the latest images have left astronomers awestruck.
The fountain of water vapor, shooting hundreds of miles into space, is sight unseen before. A colossal jet sprays a towering plume far into the cosmic void, hinting at profound mysteries beneath the moon's icy surface. Could this mean a hidden ocean? Or even life?
The Geyser on Enceladus
The geyser uncovered on Enceladus is nothing short of a cosmic spectacle. This gigantic fountain of water vapor, with its immense size and extraordinary range, sprays a watery plume so high that it reaches hundreds of miles into space.
Imagine a water jet so potent, it surpasses the height of the tallest earthly skyscrapers by a staggering margin. It's akin to a massive geyser in Yellowstone National Park, but on a scale so colossal, it boggles the mind.
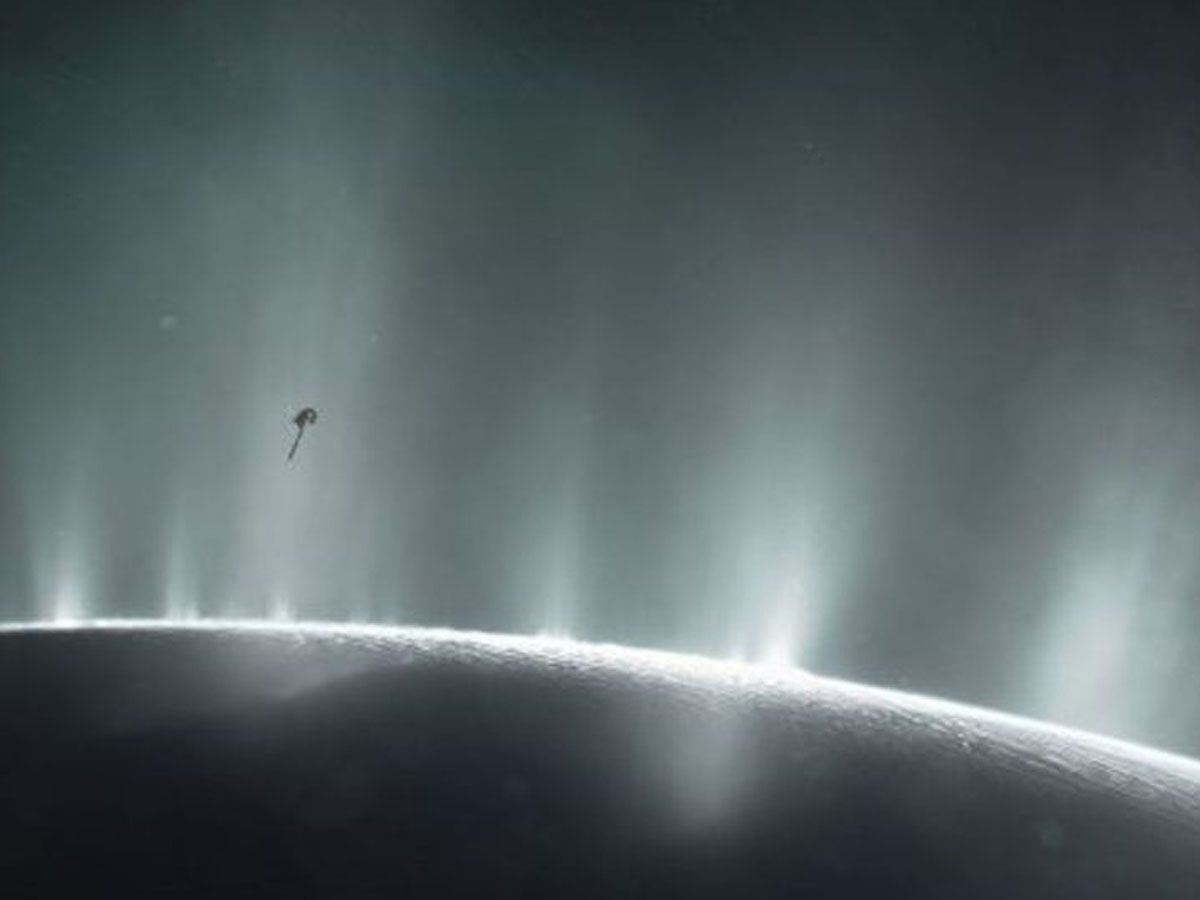

This geyser is not merely an exciting celestial spectacle. It holds immense scientific significance. Its size and range hint at powerful geological processes at work beneath Enceladus's icy shell.
Astronomers believe that the water jet's composition and magnitude could provide valuable insights into the moon's subsurface conditions, potentially unveiling the existence of a hidden ocean, and even the ingredients necessary for life.

Unraveling this secret was a feat made possible by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). Equipped with a suite of advanced instruments, the JWST boasts a wider perspective and a higher sensitivity than any previous space telescope. These attributes proved crucial in capturing this enormous plume on Enceladus, illuminating a spectacle that remained hidden from our eyes until now.
Conference and Upcoming Research
The astonishing discovery made by the JWST stirred significant discussion at a conference held at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. Researchers from across the globe gathered to ponder the intriguing findings, sharing theories and interpretations about the gargantuan geyser.
Sara Faggi, a planetary astronomer at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, labeled the discovery as "immense", highlighting the potential implications this finding could have on our understanding of outer space's celestial bodies. The conference was a hotbed of intellectual exchange, igniting discussions about the possibilities of life in the universe.
Dr. Sara Faggi is a planetary scientist & astronomer at @NASAGoddard and research assistant professor at @AmericanU. On Webb, her work has focused on analyzing spectral data from solar system objects such as comets, icy moons (e.g. Enceladus and Europa), and Mars. pic.twitter.com/JpabOPmCp8
— NASA Webb Telescope (@NASAWebb) March 8, 2023
In addition, a full research paper detailing this exceptional discovery is underway. This study aims to delve deeper into the findings, comprehensively analyzing the geyser's characteristics and the conditions on Enceladus. It promises to deliver a wealth of information, further solidifying our understanding of Saturn's intriguing moon and its extraordinary water vapor plume.
Understanding Enceladus: A Brief History of Enceladus Discoveries
Enceladus, measuring about 313 miles in diameter (which is almost the same distance as traveling from Los Angeles to San Francisco), is a petite satellite among Saturn's array of moons.
Its dazzling, ice-coated exterior has sparked significant interest within the scientific community. However, the most compelling revelation about this cosmic body came to light in the year 2005.
While making its rounds of the Saturn system, NASA's Cassini spacecraft detected peculiar 'watery blasts' emerging from this icy moon. These powerful jets were not just transient sprays of vapor. They were strong enough to form a part of Saturn's rings, a spectacle in and of itself.
The significance of these watery vapor jets was not lost on the scientific community. They were concrete indicators of active geological processes beneath Enceladus's frigid surface, raising questions about the moon's interior.
Furthermore, these jets propelled particles at high speed, creating a towering plume of icy crystals and gases, offering astronomers a window into the moon's interior chemistry.
Chemical Composition and Potential Life
The most intriguing part of the jets, perhaps, was their chemical makeup. Detailed analysis revealed the presence of methane, carbon dioxide, and ammonia, along with water.
These molecules, fundamental building blocks for life as we know it on Earth, suggested a tantalizing possibility. Could there be conditions favorable for life beneath the icy shell of Enceladus?
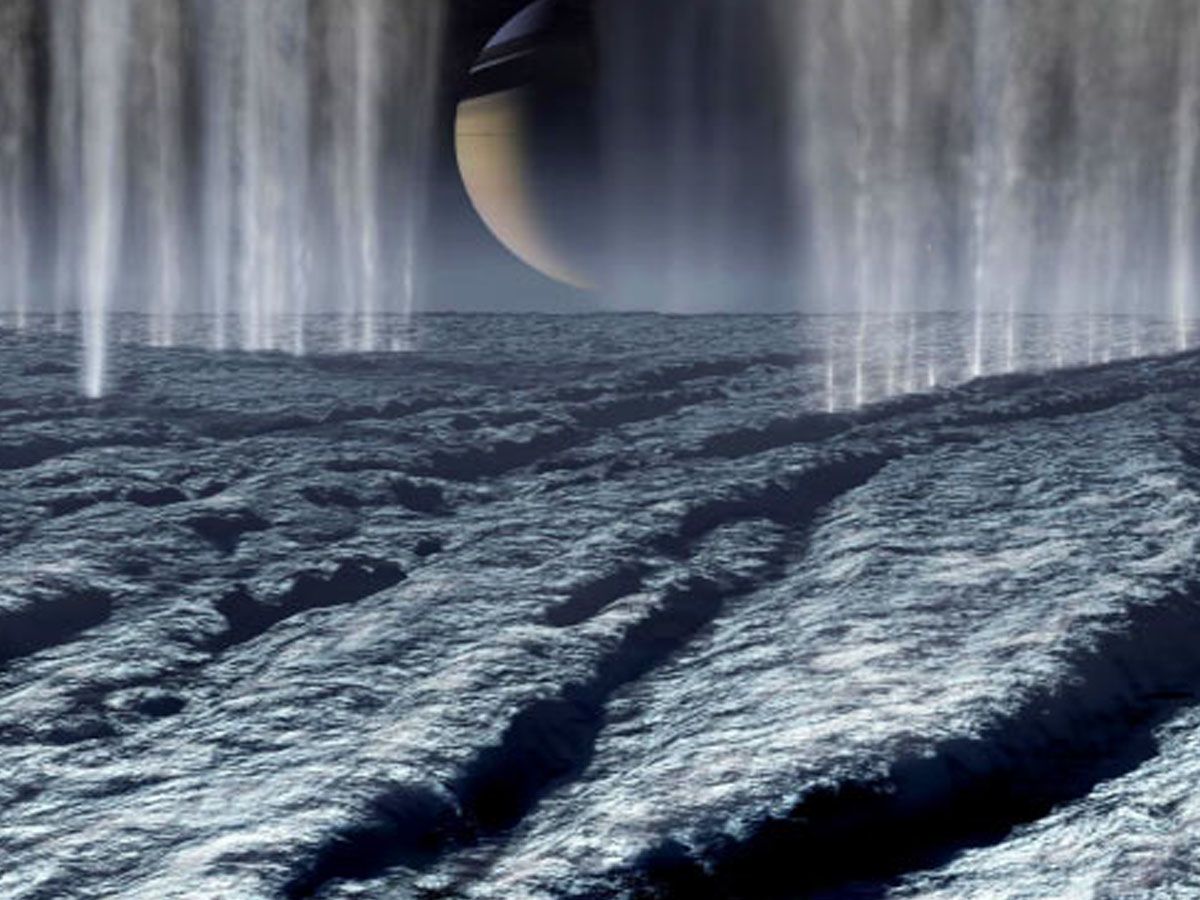

The detection of these organic molecules stirred the scientific community, setting the stage for intense debates and speculation. The presence of these gases, particularly in conjunction with water, pointed to the intriguing possibility that some form of life could exist, or might have existed, beneath Enceladus' icy surface.
The Structure of Enceladus
Peering into Enceladus's icy exterior, scientists speculated about the existence of a hidden ocean beneath the moon's ice-encrusted surface. Indicators, such as variations in the moon's rotation and the composition of the jets, pointed toward the existence of a subsurface body of water.
And where was the water for the gigantic geysers coming from? The most probable answer pointed towards hydrothermal vents on the ocean floor. Much like the ones found in Earth's oceans, these vents could be the source of the water spurts, heated by geological activity in Enceladus's core.
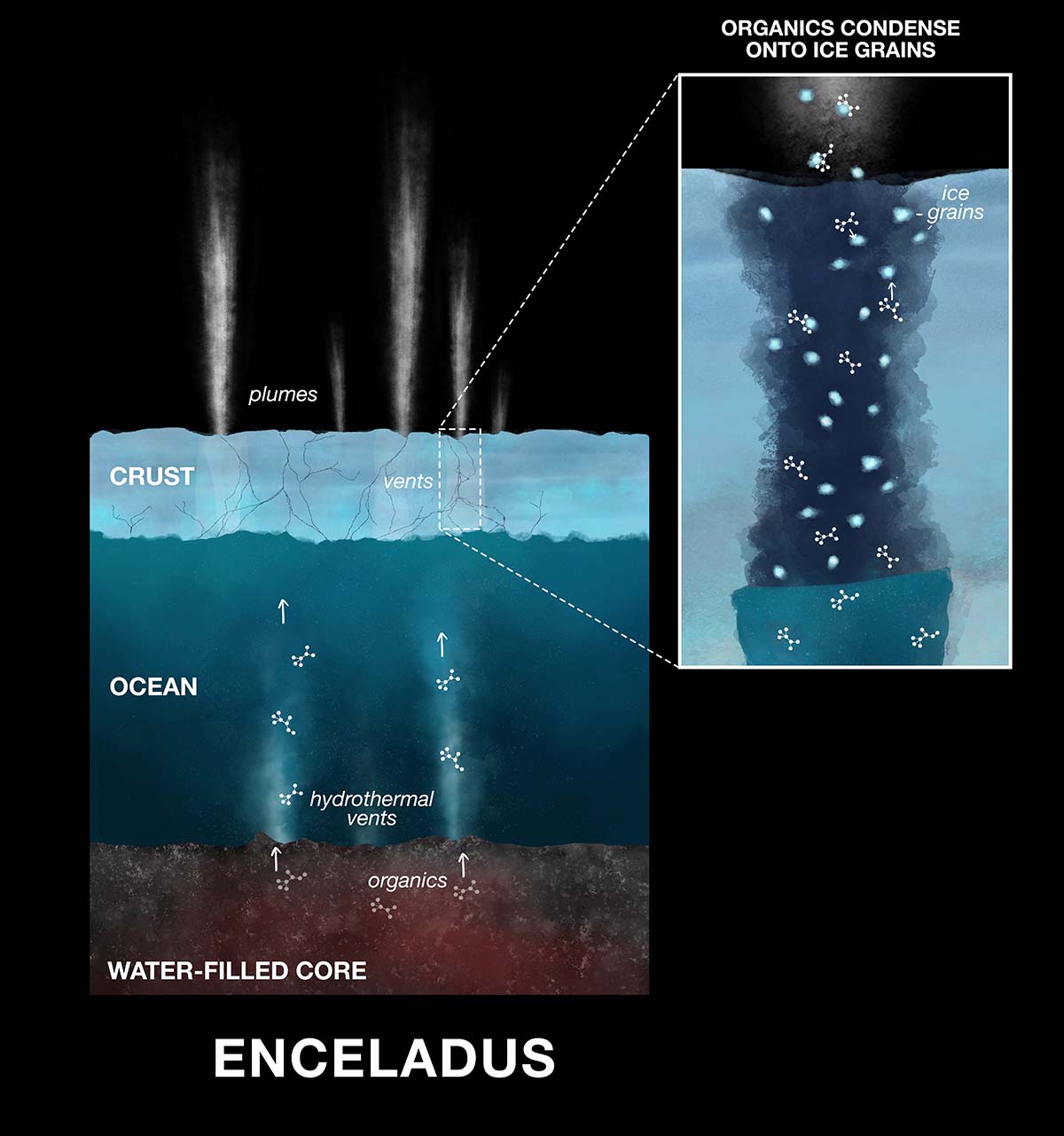
This complex interplay of the icy surface, hidden ocean, and active geological core painted a fascinating picture of Enceladus. A moon that was more than just a pretty spectacle in the night sky, it was a world with its own dynamic processes and potential secrets, waiting to be unraveled.
Future Missions to Enceladus
As Enceladus continues to reveal its fascinating features, NASA has its eyes set on future return missions, seeking to unlock the moon's enigmatic secrets. The presence of organic molecules, coupled with a potential subsurface ocean, has ignited interest in exploring Enceladus for signs of life.
The Enceladus Orbilander Mission
First on NASA's agenda is the ambitious Enceladus Orbilander Mission. This innovative venture aims to send a spacecraft that will transition into a lander, settling on the moon's icy surface.
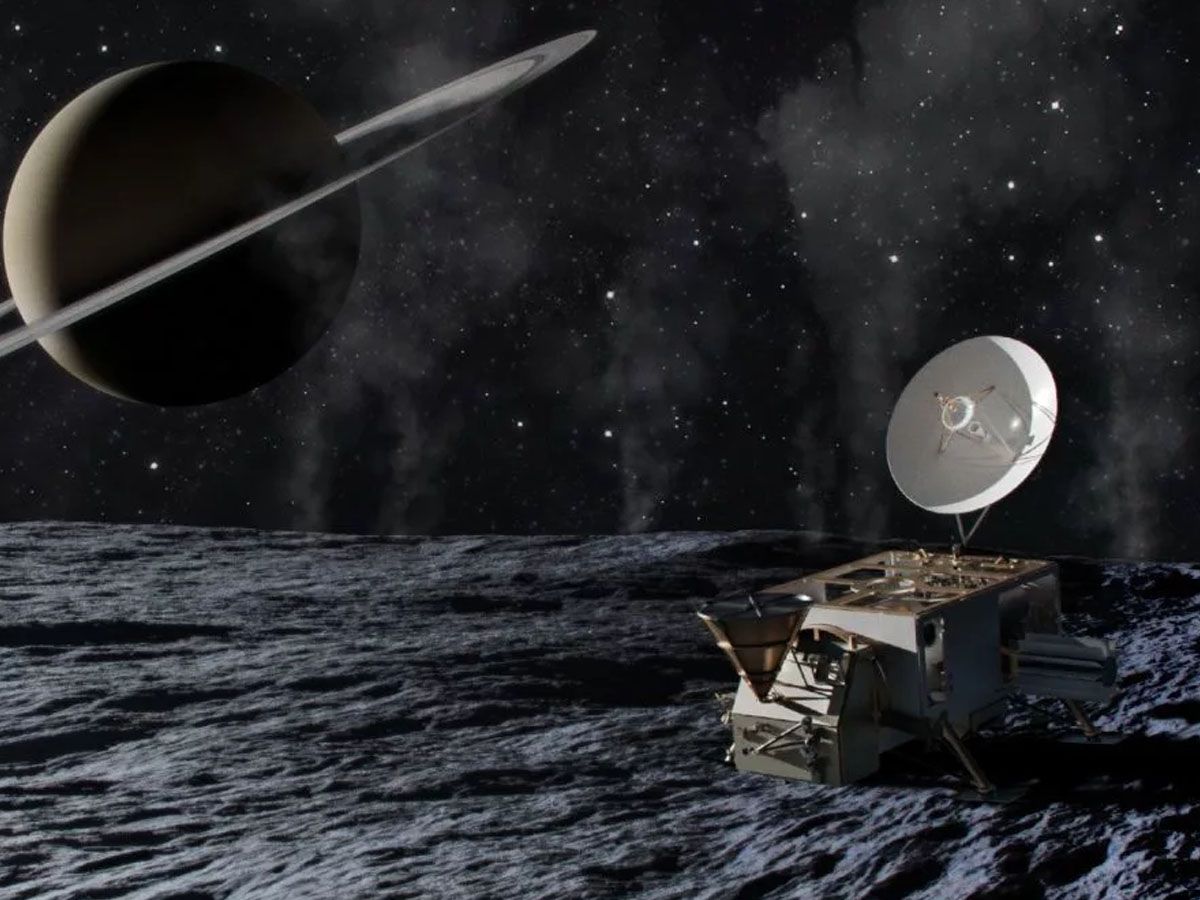

The mission's objective isn't just a cursory visit; the Orbilander will be equipped with state-of-the-art instruments, including a DNA sequencer and a microscope. These tools will enable the collection and analysis of surface samples, potentially revealing more about the moon's chemical composition and the possibility of life.
The Exobiology Extant Life Surveyor (Snake Robot) Mission
In addition to the Orbilander, NASA has proposed an entirely different mission, one that seems straight out of a science fiction novel. The Exobiology Extant Life Surveyor, or as it's fondly referred to, the "snake robot," is a testament to human ingenuity.
This autonomous robot, equipped with cameras and Lidar for navigation, is designed to slither its way across Enceladus's icy terrain and dive into the speculated subsurface ocean.
The snake robot's primary goal? To explore the ocean floor and the alleged hydrothermal vents, believed to be the source of the moon's gigantic geysers.
By studying these vents and the surrounding areas, scientists hope to gain invaluable insights into the moon's internal structure and the potential existence of life-sustaining environments.
These future missions are not just exploratory endeavors but also symbolic steps in humankind's ceaseless pursuit of knowledge and understanding. Through them, we hope to uncover the truths about Enceladus, possibly rewriting the books on where life could exist beyond Earth.
Sources: esa.int / livescience.com