Password managers play an invaluable role in our digital age, where online security is paramount, protecting login details and credit card numbers from being misused or lost. With their secure vault for password storage and management capabilities, password managers provide easy access to accounts without remembering multiple complex passwords. KeePass stands out among popular password managers due to its robust features and open-source nature. However, recent discoveries point towards significant vulnerabilities within KeePass, which seriously threaten its user security.
The discovery of this vulnerability CVE-2023-3278 came to light thanks to the diligent efforts of security researcher 'vdohney.' After meticulous examination, they uncovered a critical flaw in KeePass, exposing a potential avenue for attackers to compromise the master password of its users. To demonstrate the severity of the exploit, 'vdohney' developed a proof-of-concept tool that showcases the vulnerability in action.

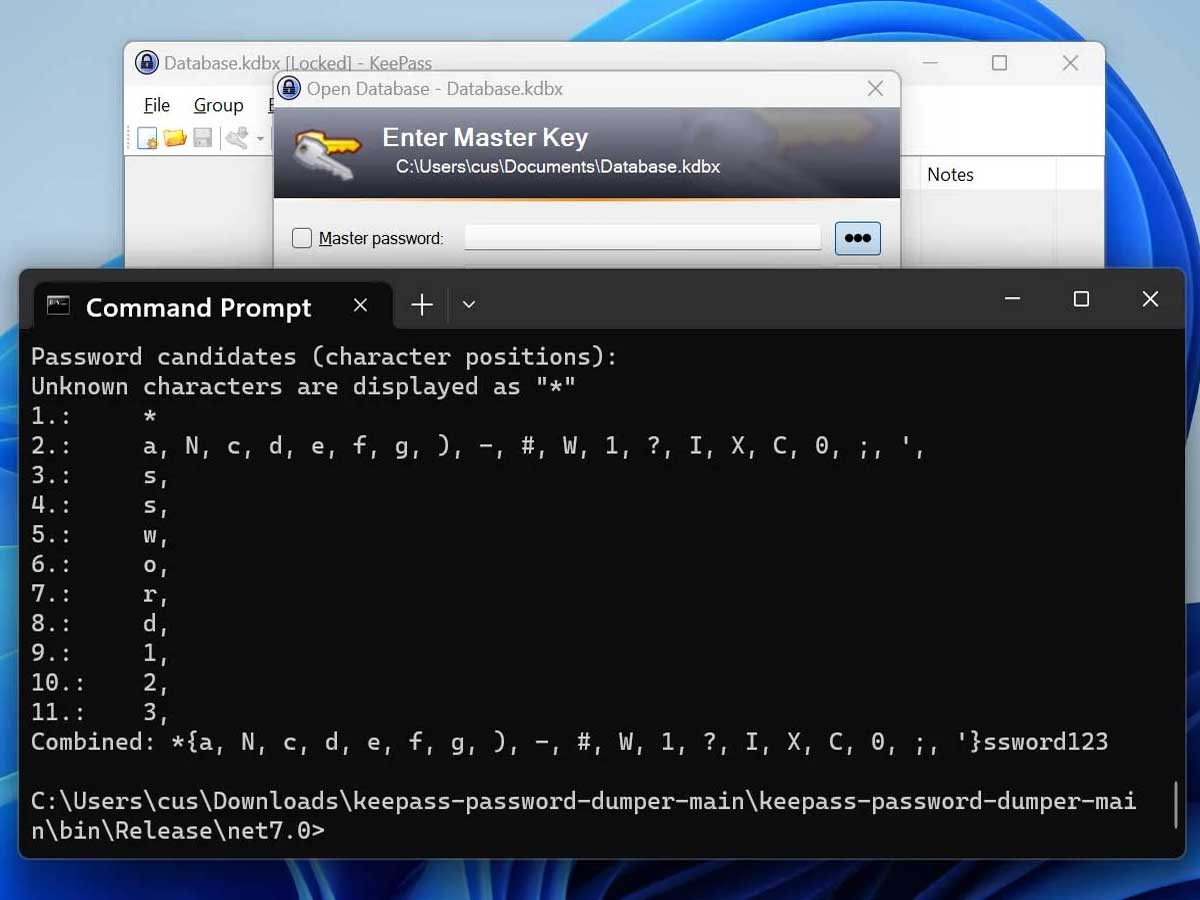
This tool, designed to exploit the vulnerability, is capable of extracting the user's KeePass master password in plaintext. Although it cannot retrieve the first one or two characters of the password, it can expose the rest, leaving the security of the entire database in jeopardy. The tool takes advantage of traces left in the system memory by a specific component within KeePass, known as SecureTextBoxEx.
To comprehend the gravity of this vulnerability, it is essential to understand how KeePass operates. KeePass employs a master password to protect its stored login information. When users enter their master password into KeePass, it unlocks the encrypted database and grants access to the stored credentials. However, this very feature that enhances security has become vulnerable.
The exploit allows an attacker to retrieve the master password from a locked or closed KeePass database. This means that the vulnerability can still be exploited even if users have taken precautions to secure their KeePass workspace, such as locking it or fully closing the program. This poses a significant threat to users relying on KeePass for password management.
At the heart of this vulnerability lies SecureTextBoxEx, a custom code implementation within KeePass. When users enter their master password using this password entry box, traces of the entered characters are left behind in the system memory. It is these remnants that the proof-of-concept tool leverages to extract the master password in plaintext, compromising the security of the user's credentials.
Although exploiting KeePass requires physical access to its target machine for success, remote access apps may still be vulnerable. Malware infection on an infected PC could dump KeePass memory dump and send it back to an attacker, thus facilitating offline extraction of the master password. Therefore, device security measures must also remain vigilant against possible malware infections.
Noteworthy is that this exploit targets KeePass specifically and is not restricted to any particular operating system. However, Windows systems appear the most vulnerable. Additionally, versions running Linux or macOS could also be vulnerable. Thus, users should remain mindful of potential threats associated with this vulnerability regardless of which OS they use.
At first learning of this critical vulnerability, KeePass developer Dominik Reichl quickly acknowledged it and is actively working on a fix for the release of version 2.54. With any luck, this fix should become available within months. Stay tuned.
KeePass 2.54 will soon offer security enhancements and testing support through a beta version giving those eager to reap its advantages an opportunity to test out and provide valuable feedback to its development team. In addition, this beta release of KeePass allows users to experience these future upgrades firsthand and give insight into what could come in later releases.
As part of an effort to counter this vulnerability, developers plan on taking additional security steps. One such measure includes including text fragments within password entry boxes that could serve to confuse any potential attackers who try to extract master password data from system memory, making any attempts more challenging to be completed successfully.
Given the serious nature of KeePass's vulnerability, users must act immediately to implement secure practices and protect passwords and sensitive information.
At all costs, be cautious when downloading apps or opening files from unknown sources since malicious files or programs may appear legitimate and put your system at risk. Furthermore, avoid websites containing harmful material or attempting to coax users into divulging personal data that could compromise it.
Antivirus software on all your devices is an integral way of combatting malware threats, providing additional layers of defense. In addition, regular updates and scans also help detect threats before exploiting any vulnerabilities in the system, offering another layer of defense and adding another level of security for added peace of mind.

Avoid sharing your KeePass master password with anyone. Instead, keep this secretive knowledge between yourself and yourself to protect the safety of your database from unwelcome visitors.
As KeePass vulnerabilities remain an immediate risk until their solution becomes available, taking immediate steps can help lower associated risks. One option is waiting until KeePass 2.54 arrives. This temporary measure should help safeguard passwords until their vulnerability can be effectively addressed.
Clear swap and hibernation files on your system as they could contain sensitive data that an attacker could exploit through exploiting vulnerabilities in system memory by regularly rebooting and reducing chances for the attack while decreasing memory usage.
In the interim, if you need to explore alternative password managers, conduct thorough research and find one that meets all your security requirements. Numerous reliable managers offer their features and benefits. Why not migrate your passwords over during this interim period?
As part of your disposal process for older devices, all data must be securely erased using encryption techniques to avoid physical attacks or data mining compromising sensitive information.

The recent vulnerability in KeePass highlights the importance of password managers for online security. Users should be cautious and vigilant, understanding the exploit and potential attack vectors. The developer's quick response and commitment to fixing the issue with KeePass version 2.54 is reassuring. In the meantime, following best practices can help protect data, including avoiding KeePass until the fix is released, being cautious when downloading apps, avoiding questionable websites, and not sharing the master password. Staying informed and practicing good cybersecurity hygiene is essential for safeguarding passwords and sensitive information.
Sources: bleepingcomputer.com / digitaltrends.com / techradar.com / cve.mitre.org













