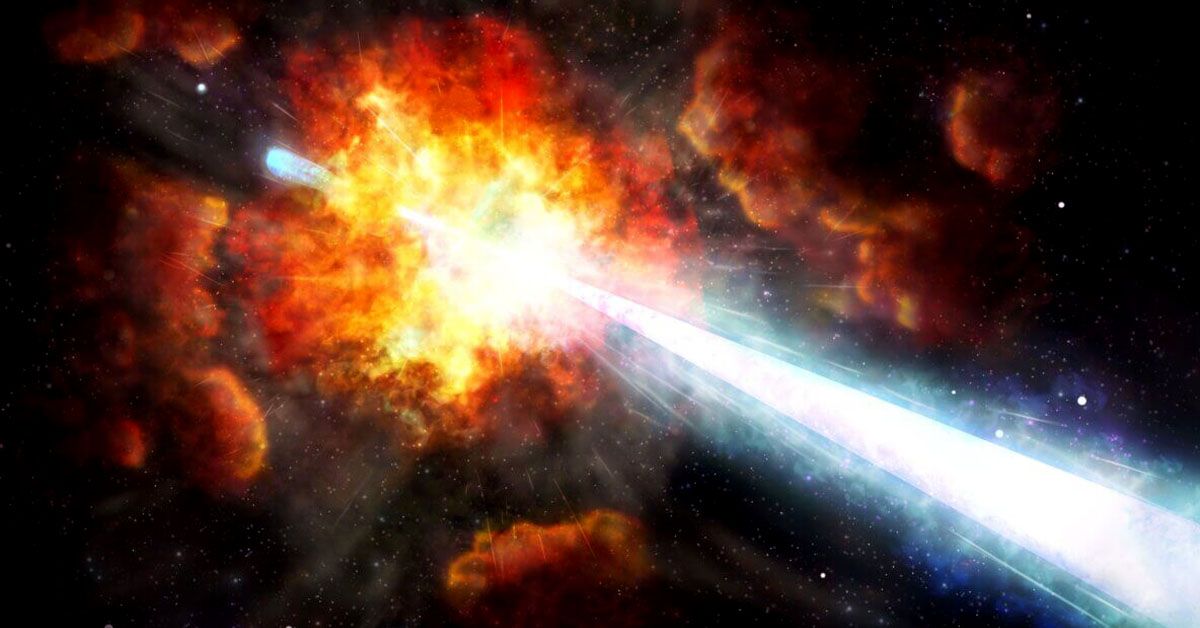
In astrophysics, nothing comes close to the thrill of detecting an extraordinary cosmic event, a flash in the cosmos so powerful that it outshines everything we've seen before. One such event labeled the Brightest of All Time (BOAT), has left scientists around the world scratching their heads, amazed by its intensity and the mysteries it presents.
This mesmerizing display occurred on October 9, 2022, illuminating the sky with a brilliant burst of gamma rays, followed by a lingering, low-fading afterglow.
But what caused this immense spectacle?
And why is this stellar explosion making scientists rethink their theories?
The Unprecedented Cosmic Event: BOAT
On a regular autumn day, October 9, 2022, an extraordinary cosmic event unfolded that made the astrophysical community sit up and take notice. The event in question is now famously known as the Brightest of All Time, or BOAT for short.
But what set this event apart from other cosmic phenomena? The hallmark of BOAT was an incredibly bright, high-energy flash of gamma rays. This burst of energy, more potent than anything previously recorded, bathed our universe in an intense glow.
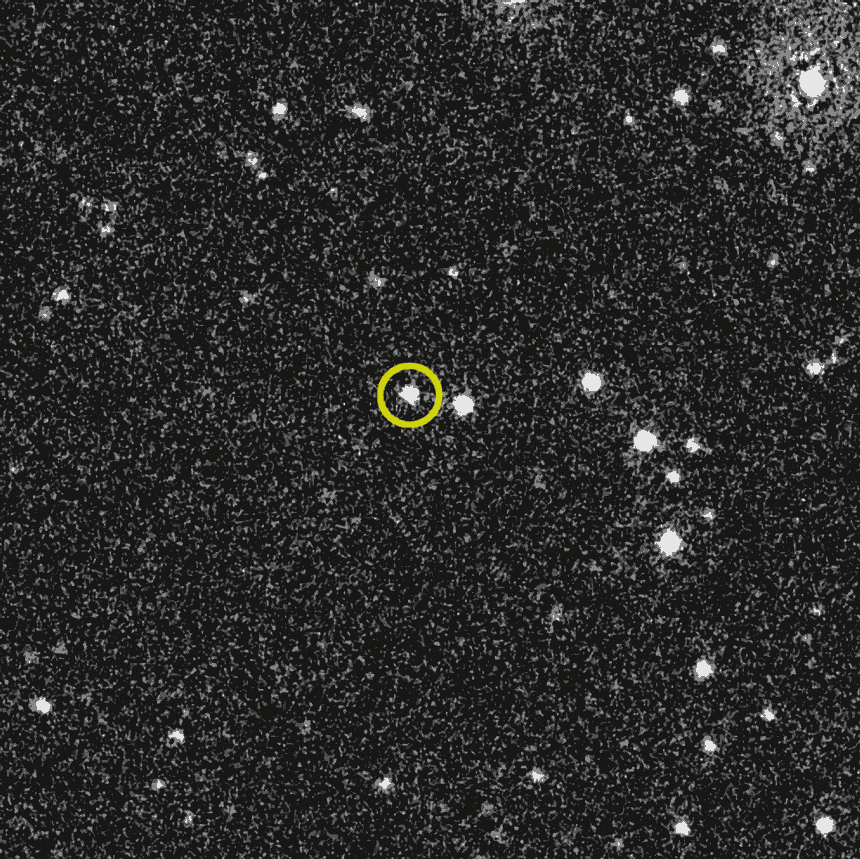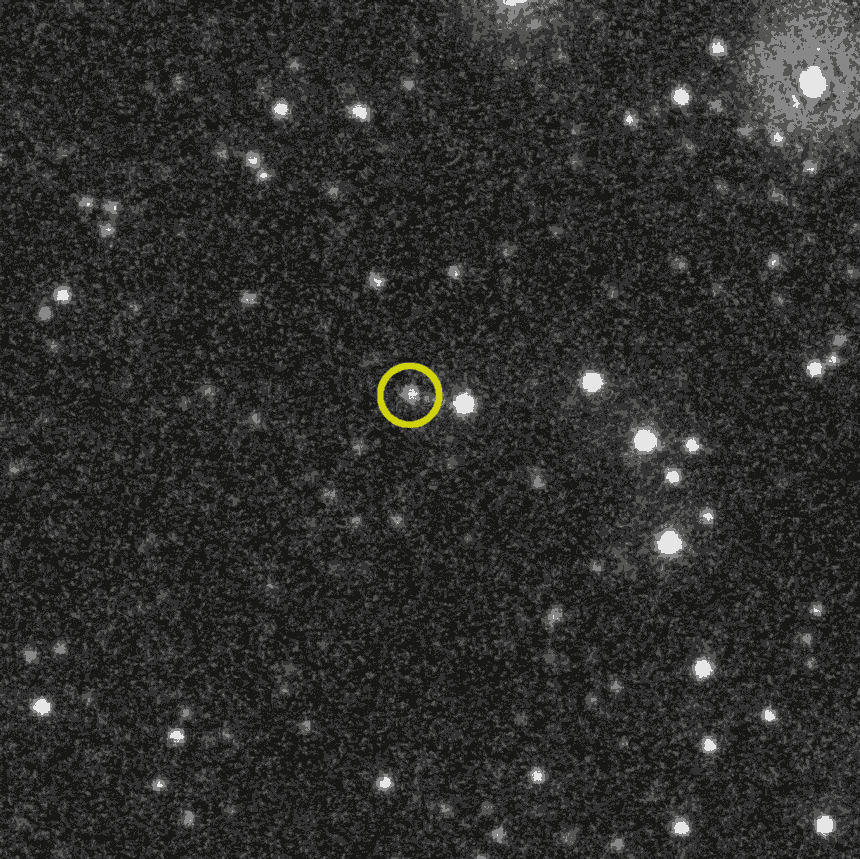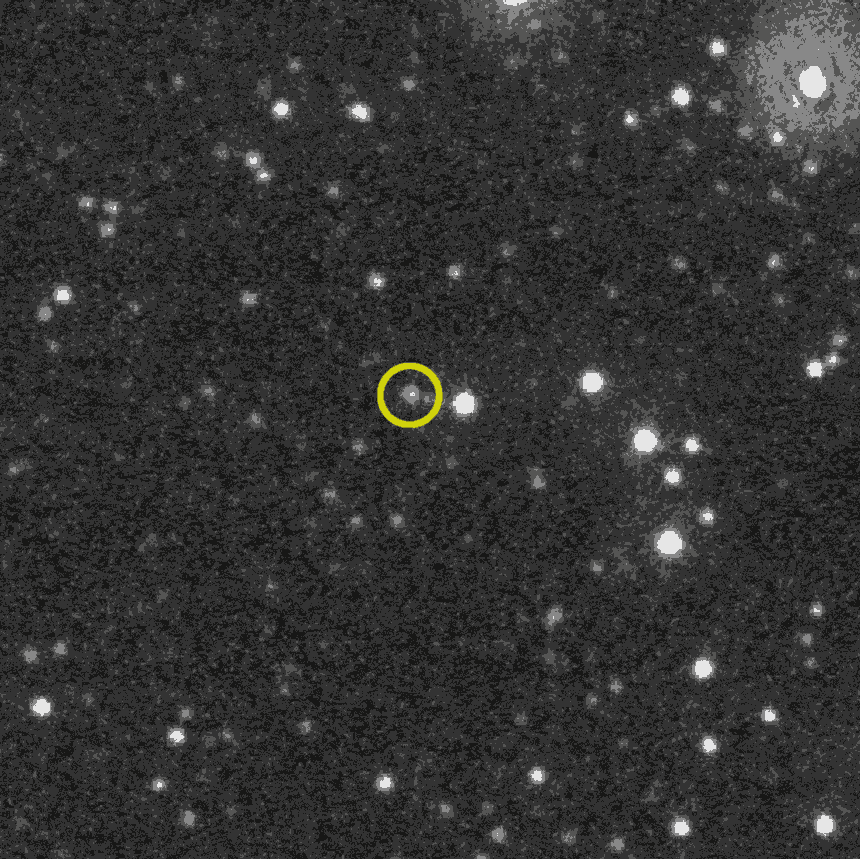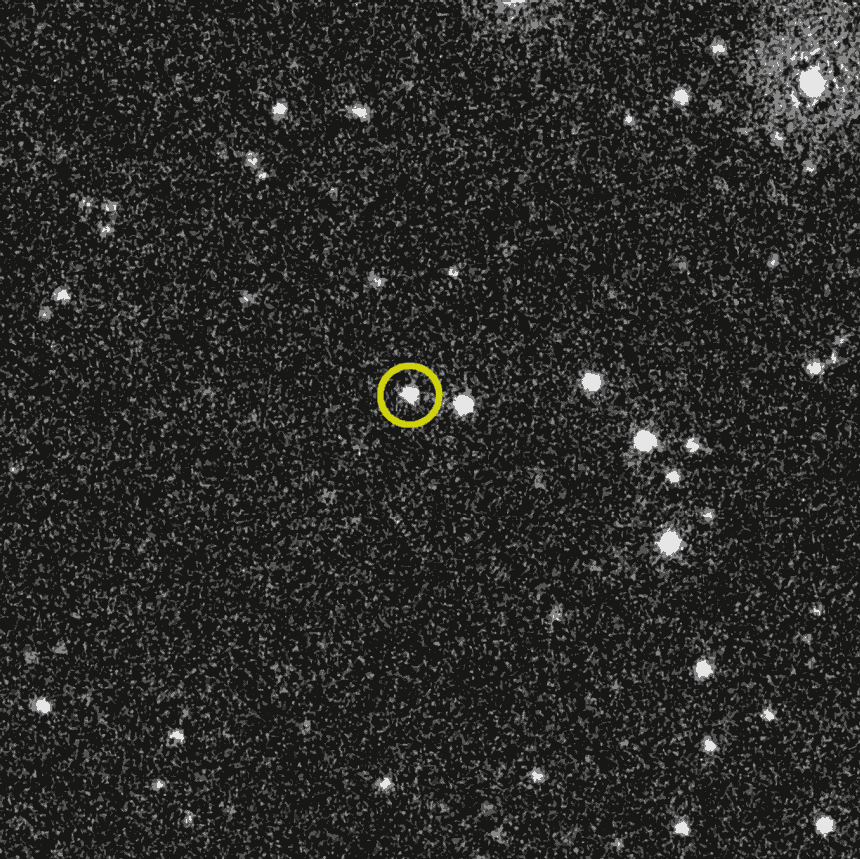
The flash, however, was only the initial spectacle. After the burst of gamma rays, BOAT refused to go quietly. Instead, it left behind a slowly fading afterglow, visible across multiple wavelengths of light.
Unlike the short-lived brightness of similar events, this afterglow lingered on, demanding the attention of onlookers from across the globe.
The Reaction of the Scientific Community
The scientific community was excited as astrophysicists worldwide quickly shifted their focus to this unrivaled spectacle. The extraordinary brightness of the gamma-ray burst (GRB) and the stubborn persistence of its afterglow made BOAT an irresistible mystery.
While fascination surrounded the event, it also presented an intricate puzzle to the scientists. Why was the gamma-ray burst so exceptionally bright? How could the afterglow continue to linger, defying the known properties of a standard GRB?
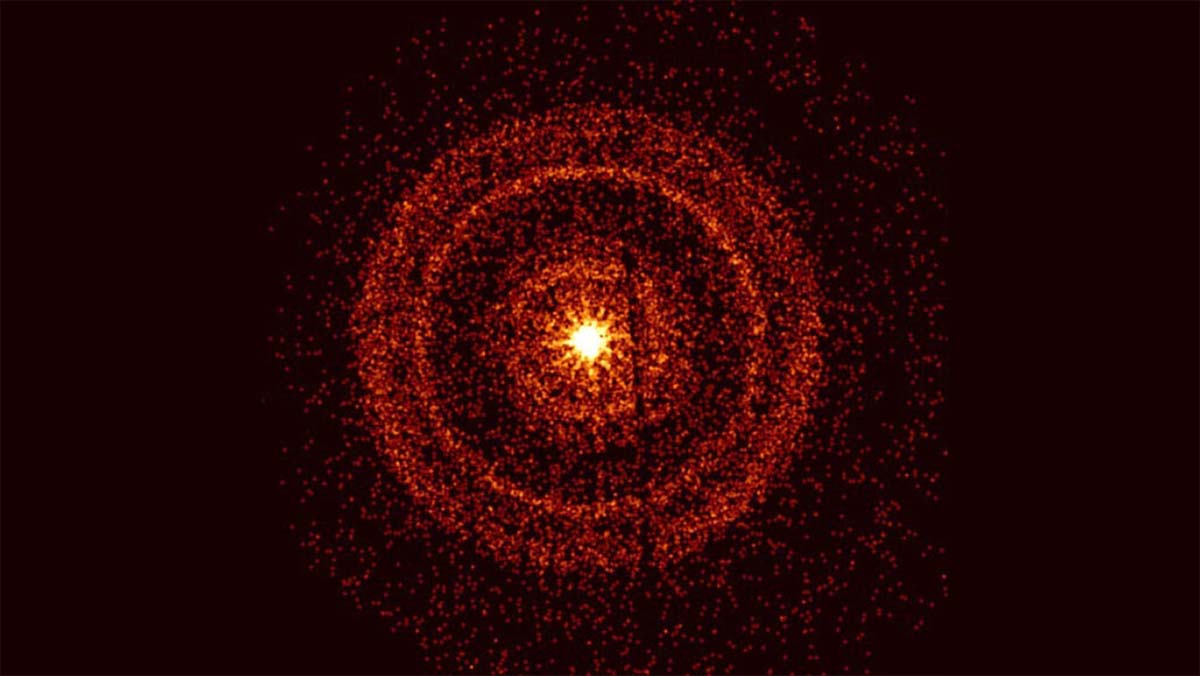

As they delved deeper, it became clear that unraveling the secrets of BOAT was no easy task. The distinctive characteristics of BOAT set it apart from other cosmic explosions, prompting the astrophysicists to embark on a journey of discovery that would challenge their existing understanding of the universe.
The Investigation and Findings of the International Research Team
Answering the call to unravel the mysteries of BOAT, a diverse team of global scientists took the reins. This international brigade of scholars was spearheaded by Dr. Hendrik Van Eerten from the Department of Physics at the University of Bath in the U.K., and Dr. Brendan O'Connor, a freshly minted doctoral student from the George Washington University in Washington, DC.

Their rigorous investigations resulted in findings so significant they were published in the esteemed journal, Science Advances.
Together, they embarked on a mission to comprehend the reasons behind BOAT's unique behavior, shining a light on a cosmic event that baffled their peers worldwide.
Initial Explanation for BOAT
Their pursuit for answers first led them to the theory of a jet of stellar material from the explosion, pointed directly toward Earth. This directionality, they theorized, could partially explain the intense brightness of the GRB we witnessed.
The jet was likened to a garden hose spraying straight at someone, leading to a highly concentrated and visible stream.
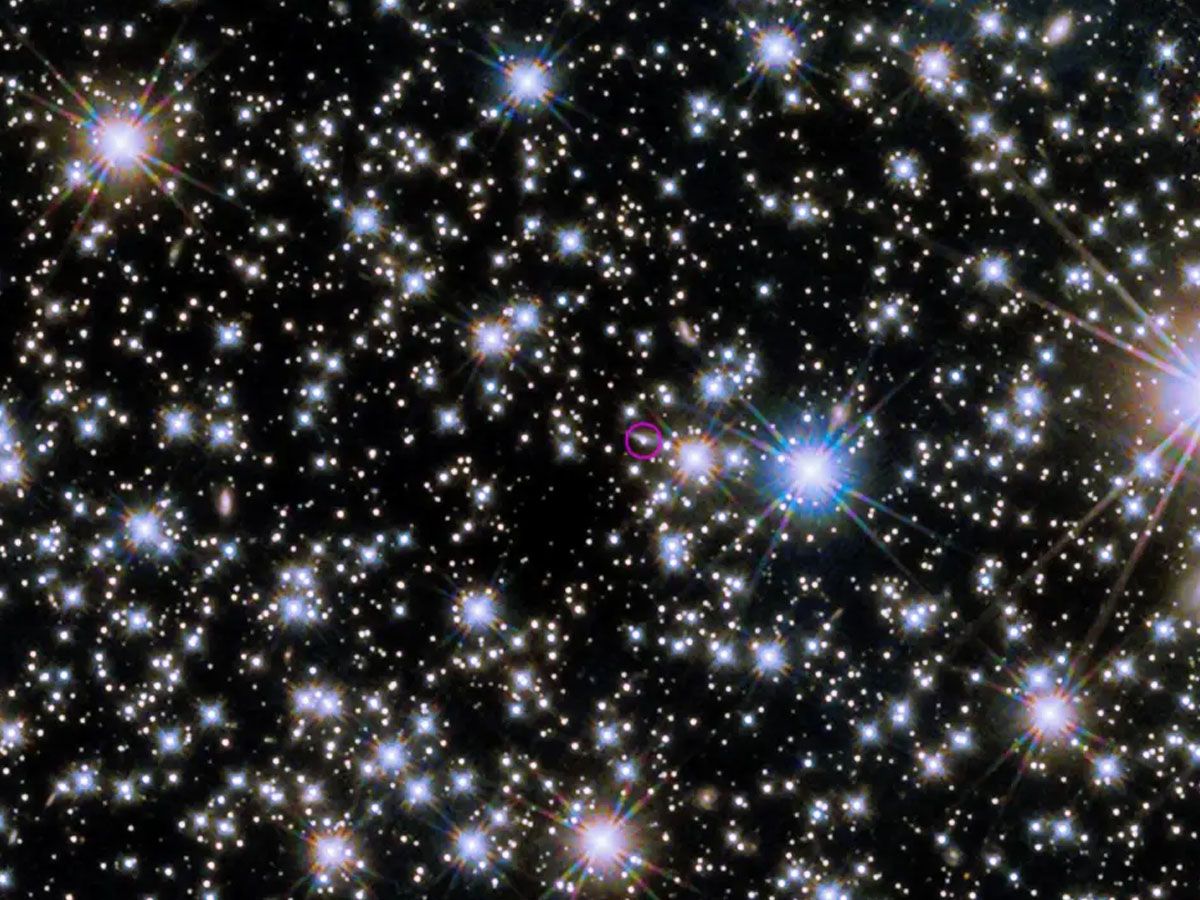

However, the team hit a roadblock when they considered the invisible edges of this cosmic jet. Traditional understanding suggested the jet's edges should be visible, but in the case of BOAT, this wasn't so.
This posed a new riddle for the team to solve, further complicating the intriguing saga of BOAT.
Unraveling the Mystery of the Afterglow
Their journey didn't end there. The lingering afterglow of BOAT proved to be another enigma. Its slow fade contradicted the characteristics of a standard narrow jet of gas, which should have dissipated rapidly.
To account for this disparity, the team introduced a novel theory. Their mathematical models suggested that the GRB had a unique structure, consisting of a narrow jet enveloped within a broader outflow of gas.
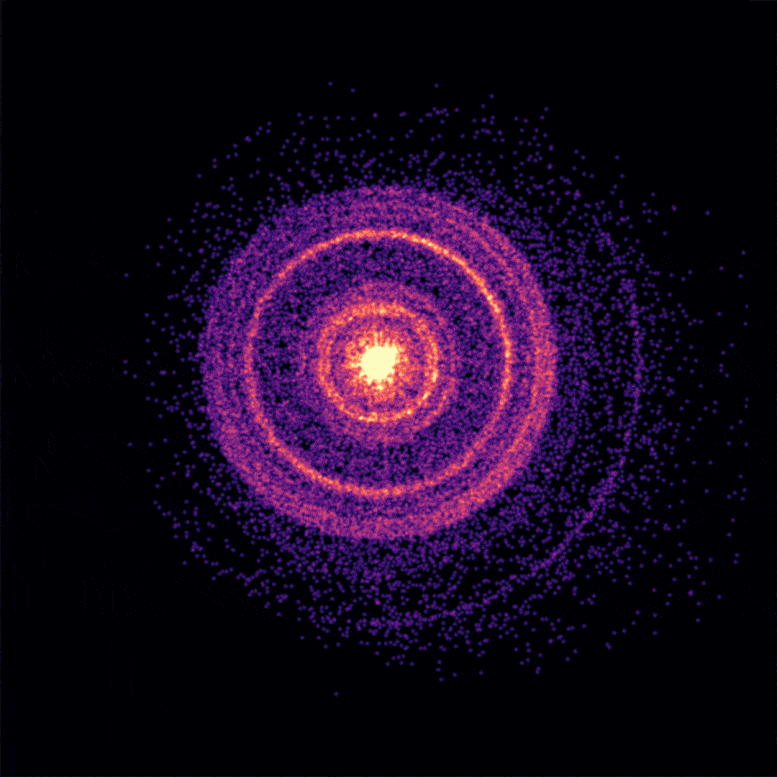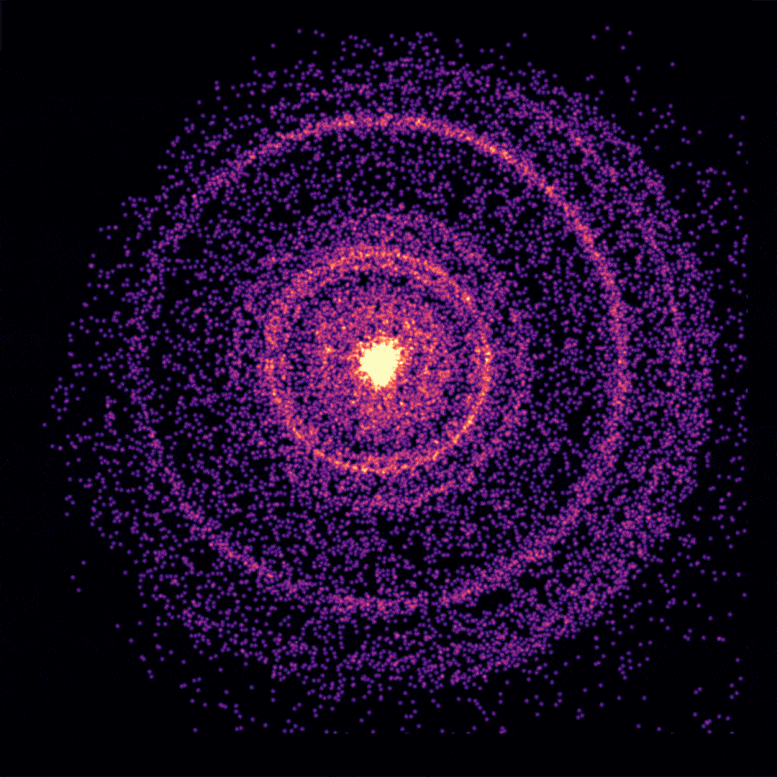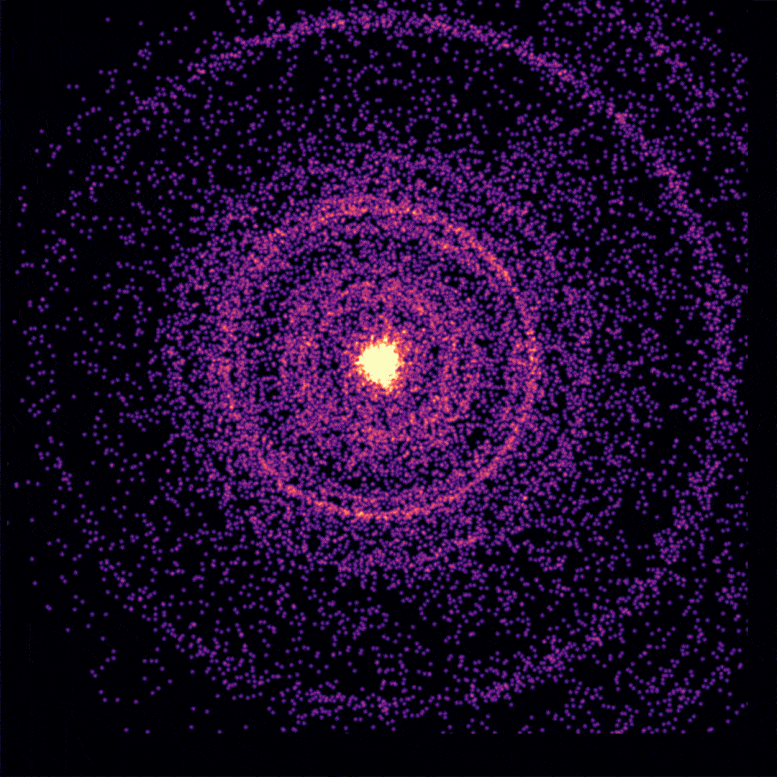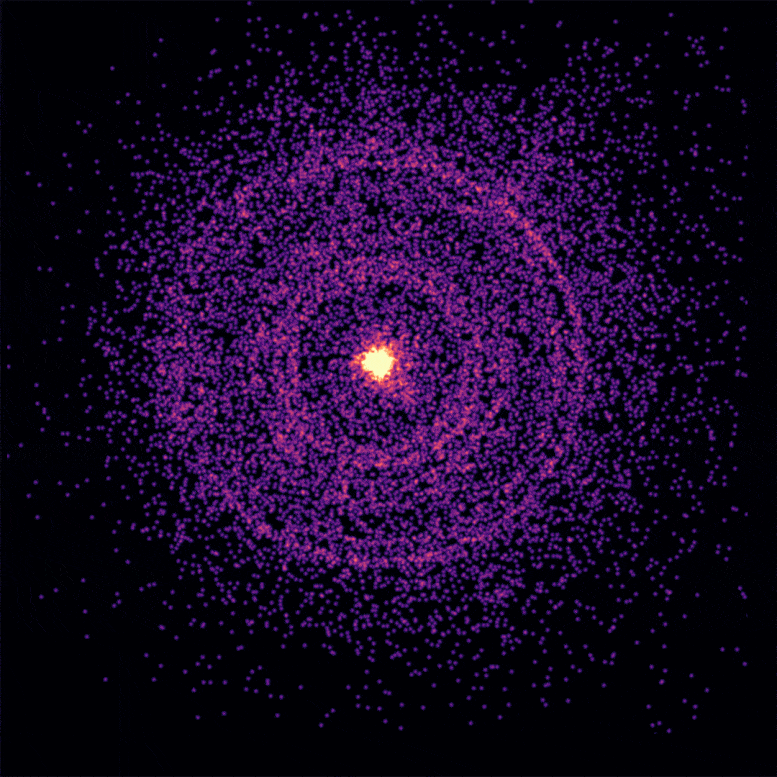
This broader structure was a product of significant mixing between the stellar material and the jet during the collapse of the star, leading to a spectacle unlike any other seen before.
This ingenious explanation, they proposed, accounted for the persistent afterglow. According to Dr. Van Eerten, the shock-heated gas continued to appear in our line of sight throughout the emission from the afterglow, ensuring the signature of the jet was not lost, thus providing an enduring cosmic show.
The Importance of the Findings
The international team's pioneering research unraveled intriguing aspects of the BOAT event, casting light on several unexplained phenomena in astrophysics. Their findings about the unique jet structure and wider gas outflow provided a novel perspective on other exceptionally bright bursts observed in the past.
Much like BOAT, these previous events lacked a clear jet signature, puzzling astronomers and defying conventional understanding.
The team's model suggested the existence of a unique category of events, ones with extreme characteristics so powerful they manage to conceal the directed nature of their gas outflow.
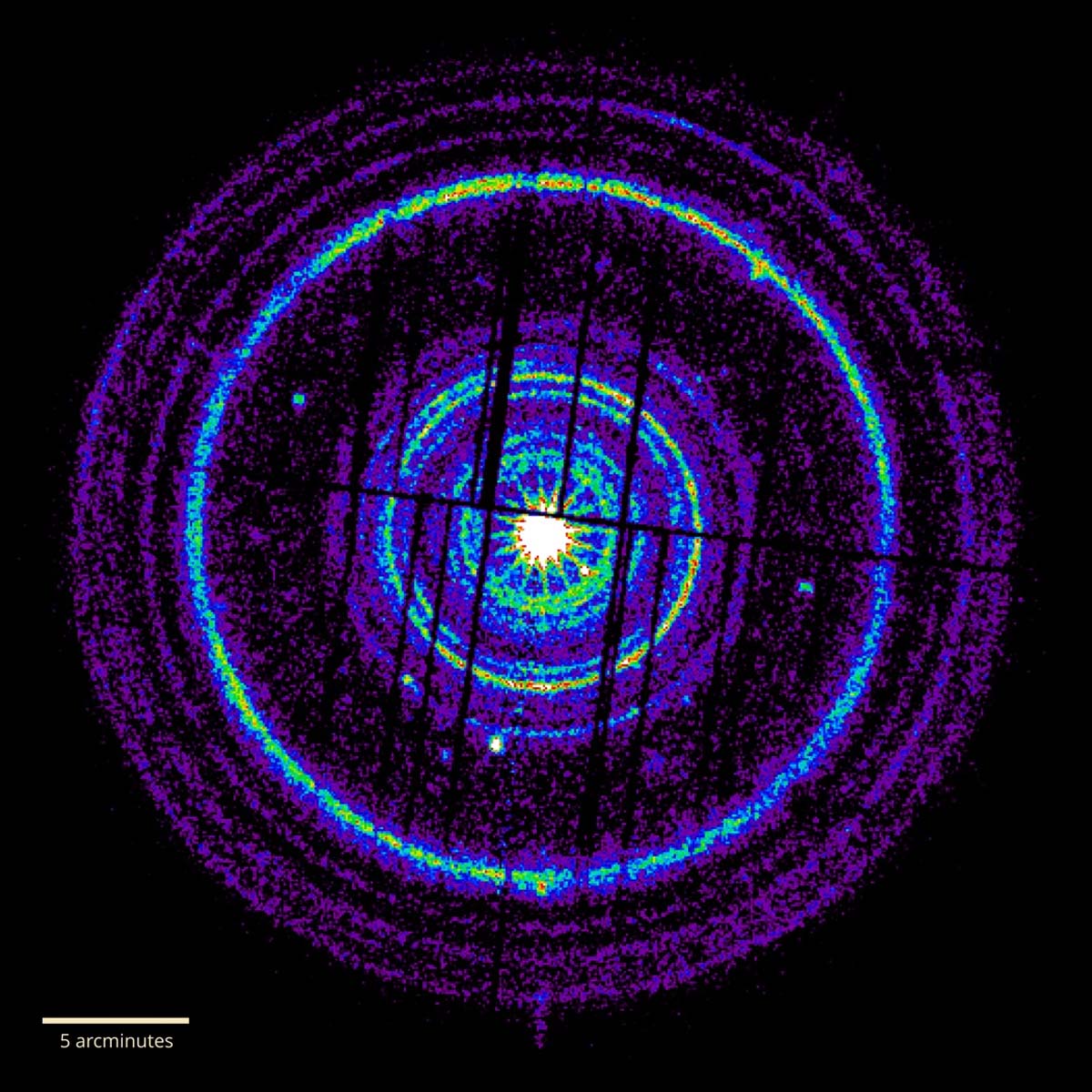

This groundbreaking idea added a new layer to our understanding of cosmic explosions and their varied natures.
Their work also laid the foundation for future investigations. Researchers now have a new path to explore the magnetic fields responsible for launching these intense jets.
The characteristics of the massive stars hosting these GRBs can also be scrutinized further, potentially revealing why such overpowering events are a rarity in the universe.
The Unique Opportunity Presented by GRB 221009A
GRB 221009A, the official designation for BOAT, is more than just a fascinating cosmic spectacle. It's record-breaking brightness and persistent afterglow present an unrivaled opportunity for the scientific community.
This extraordinary event can help us address some of the most fundamental and challenging questions in astrophysics.
With GRB 221009A as a reference point, scientists could gain insights into the elusive process of black hole formation.

This event provides a peek into the violent end of a star and the birth of a black hole, the details of which are still shrouded in mystery.
The unorthodox characteristics of GRB 221009A also present a unique chance to test dark matter models.
Dark matter, an enigma that constitutes a significant part of our universe yet remains invisible and largely unexplained, can be studied in a new light, thanks to BOAT.
Challenges Posed to Established Theories
BOAT, with its extraordinary features, has sent ripples through the field of astrophysics, forcing scientists to question long-standing theories. One such challenge comes from BOAT's non-compliance with the standard physics assumed for GRBs.
Traditionally, GRBs were thought to be straightforward events - a narrow, fast-moving jet of energy and matter, emanating from a dying star. But the BOAT event turned these assumptions on their head, showing that GRBs can be much more complex and varied.
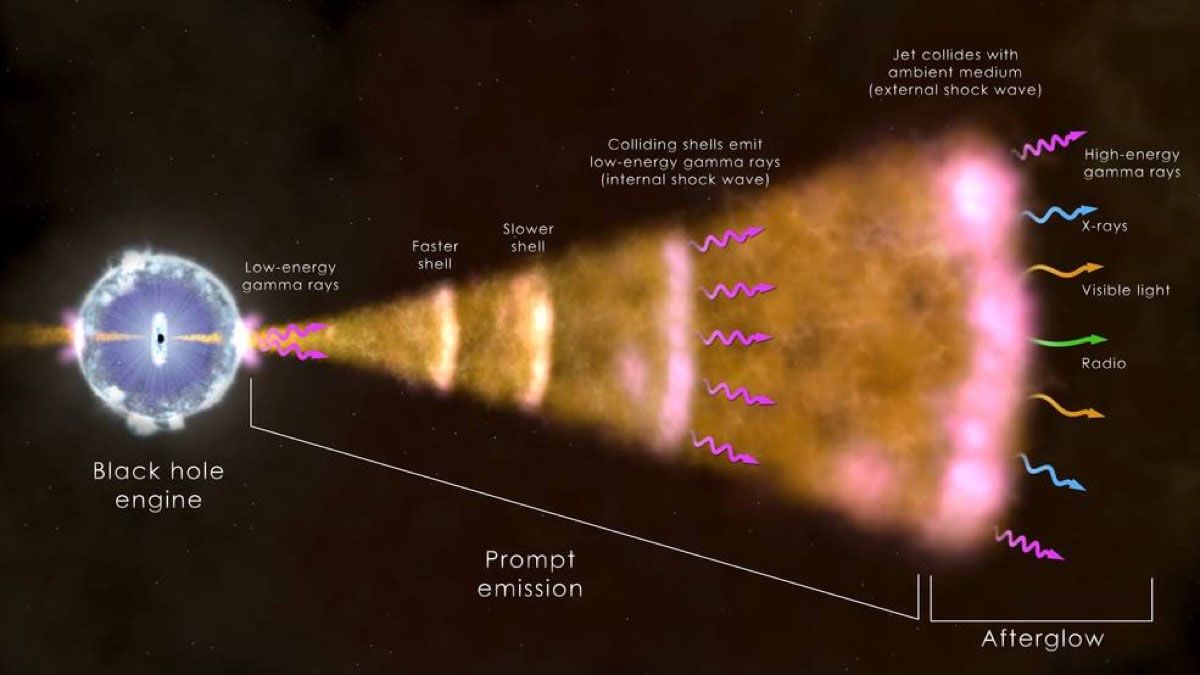
The unique structure of BOAT's jet, with a narrow core embedded in a wider outflow of gas, is unlike anything previously observed. This peculiar characteristic challenges our fundamental understanding of GRBs, demanding a fresh perspective.
Adding to the challenge, BOAT has led scientists to reevaluate theories about relativistic outflows. These are high-speed jets of energy and matter that move at a significant fraction of the speed of light.
The complex behavior exhibited by BOAT forces a revision of these theories, leading to a more nuanced understanding of such cosmic explosions.
The Step Forward in Understanding GRBs
While BOAT poses challenges, it also represents a massive step forward in our understanding of GRBs. The distinctive characteristics of BOAT have provided new insights that can contribute significantly to modeling the structure of GRB jets.
With BOAT as a reference, scientists can start to build more complex models of GRB jets, accounting for scenarios where the jet and the stellar material intermix, leading to a broader outflow.
These models will undoubtedly enhance our understanding of GRBs, allowing us to predict and explain their behavior better.
This journey into uncharted territory will require detailed computer simulations capable of modeling the incredibly complex and dynamic systems at play during a GRB.
This event underscores the need for advanced computational tools in astrophysics, driving innovation in this crucial area.
BOAT has had a profound impact on the field of astrophysics. It has not only challenged existing theories but also provided a roadmap for future research, promising a deeper understanding of the fascinating yet enigmatic phenomena of the cosmos.
Sources: science.org












