We've recently heard a lot about Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). It's like the superstar in the world of artificial intelligence (AI). AGI, aka Artificial General Intelligence, is a big deal because it's trying to be as smart as humans but inside a computer program. So, what's the scoop on AGI, and what's it gonna do in the future?
Well, AGI is basically AI that's shooting for the stars. Like Techtarget says in there article, It wants to do everything a human brain can, like learning on its own and solving mind-boggling puzzles all by itself.
This is different from the General Intelligence you see around, the one we call Weak Artificial Intelligence or simply Weak AI. Weak AI, it's like having a one-trick pony. It's good at one thing and only a little else. But AGI, it's more like a jack-of-all-trades. It's here to tackle all sorts of problems, no matter how tricky or different they are. AGI is like the ultimate AI dream.
Understanding AGI

Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is quite the buzzword in the world of artificial intelligence (AI). But what does it really mean? Let's break it down.
AGI refers to Artificial Intelligence systems that are designed to be on par with human cognitive abilities. We're talking about Artificial Intelligence that can think, learn, and problem-solve just like we do. Imagine a computer program that not only processes data but also comprehends it, learns from it, and can tackle unfamiliar challenges. That's the essence of AGI.
One of the defining features of AGI is its self-teaching capability. Unlike traditional AI, which requires extensive human programming for each task, AGI can learn on its own. It's like having a virtual student who doesn't need a teacher; it figures things out as it goes.
Now, here's where it gets interesting. AI researchers, the brilliant minds behind all this, have mixed feelings about AGI. Some are optimistic, believing it's the next frontier in AI evolution. Others are skeptical, questioning if achieving true AGI is even possible. So, you've got a bit of a debate going on in the AI world.
Can we really create machines that think and learn like humans? That's the million-dollar question.
Strong AI versus Narrow AI
Let's dive into the battle of the AIs, shall we? On one side, we've got Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), also known as Strong AI. And on the other side, meet Weak AI. They're both AI but like distant cousins rather than siblings.
AGI is the Einstein of AI. It's the big brain in the family. What sets it apart is its ability to function autonomously. Think of it as your super-smart friend who can tackle any problem you throw at them, even if they've never seen it before.
What is The Turing test?
When we talk about AI, we must mention the Turing test, which was originally coined as the imitation game by the brilliant mind of Alan Turing back in 1950.
This test is all about gauging whether a machine can pull off a rather remarkable feat – mimicking human intelligence. Speaking of Turing, he's the same English computer scientist, cryptanalyst, mathematician, and theoretical biologist who laid the foundations for this intriguing challenge.
Basically, the Turing test answers a fundamental question: Can a computer think like a human? Fast forward to June 2014, a significant moment occurred when a computer AI named Eugene Goostman achieved the unthinkable – it passed the Turing test.
Developed by a team of three programmers, including the talented Eugene Demchenko, this AI managed to convince 30 human interrogators of its humanity.
AGI aims to mimic human intelligence, and that includes the capacity to learn, adapt, and excel in various tasks. It's the kind of AI that can read, comprehend, and improve upon human-generated code. It's got abstract thinking, common sense, and transfer learning in its toolbox.
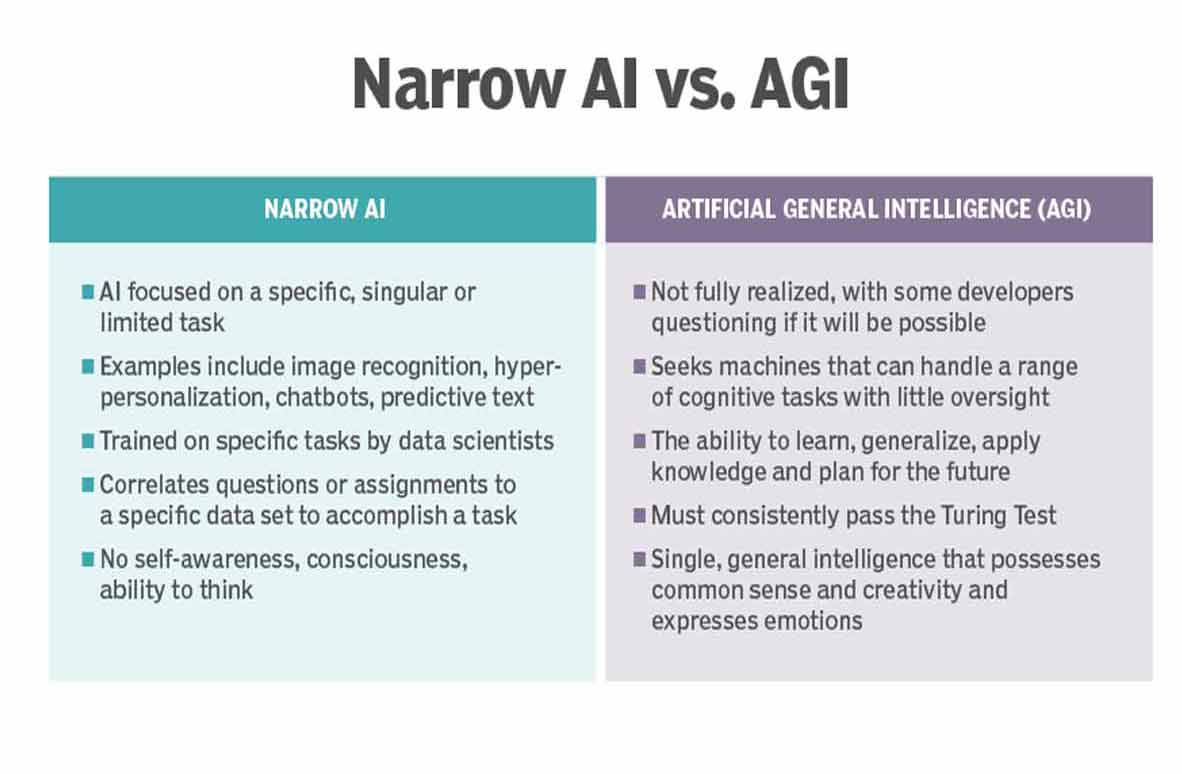
Now, let's talk about Weak AI. This AI isn't weak in the sense of being powerless. It's more like specialized AI. It's designed for specific tasks, and it sticks to its lane. You've probably encountered Weak AI without even realizing it. Have you ever used a self-driving car? That's powered by Weak AI. Are you chatting with a friendly chatbot online? Yep, that's also Weak AI at work.
The key distinction here is that Weak AI doesn't have the capacity to go beyond its programming. It's like having a super-skilled worker, but they can only do one specific job really well. They can't switch gears and become an expert in something entirely different. AGI, on the other hand, is versatile. It's the AI equivalent of a polymath. If you want more AGI examples, you should read Investopedia's article.
The Road to AGI
Approaches to AGI Development
So, how do we actually get to Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)? It's like trying to build a spaceship to another galaxy – it's a complex journey, and there are different routes to explore.
AGI Development Approaches: Think of these as the roadmaps to creating AGI. There isn't just one way; researchers have a few strategies up their sleeves.
One approach is the use of neural networks and deep learning. These are techniques inspired by the human brain. The idea is to create AI systems that mimic how our brains work. It's like trying to build a brain in a box. These systems can process vast amounts of data and make sense of it, which is a big part of what AGI needs to do. In this path to AGI never forget IBM company.
What is Deep Learning?
Before we start discussing All the Artificial intelligence, General Intelligence, and Weak AI, We have to talk about Deep Learning and Machine Learning.
The easiest way to explain Deep Learning is that it is one of the more alluring branches of machine learning and explores artificial neural networks with stunning precision to simulate how human minds work. At its heart, deep Learning relies on data collection as its driving force to enable computers to understand large volumes of information efficiently and quickly.
Deep Learning's hallmark lies in its mysterious depths, hidden layers that fine-tune precision while unlocking automation potential for today's AI innovations.
Consider that everyday items like digital assistants and autonomous vehicles rely heavily on deep Learning's prowess for success. What sets deep Learning apart from conventional machine learning, you ask? Well, deep Learning excels at handling both structured and unstructured data sources efficiently, extracting features seamlessly without manual manipulation of information!
It takes the burden out of manual data handling by being an efficient data processing platform that handles everything automatically for us. Deep Learning can give your data analysis magic! Deep Learning encompasses various learning styles: supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning all offer unique capabilities for processing information.
Backpropagation and forward propagation processes combine in an intricate ballet, honing deeper learning into an intimidating but effective weapon.
Real-world applications of deep learning span across sectors like law enforcement, financial services, customer service, and healthcare, taking on roles like speech recognition systems or medical image analysis as examples of its magic in action.
Deep learning hardware investments should also be expected; remember this when witnessing jaw-dropping speech recognition or medical image analysis systems at work!

Another approach is computational neuroscience. Here, scientists try to understand the brain's structure and function. If they can recreate the brain's wiring and processing in a computer, it might lead to AGI. It's like reverse engineering the brain.
What is a Neural Network?
When we discuss about deep learning, we have to mention neural networks. Basically, a neural network is a technique used in the field of advanced artificial intelligence that aims to replicate the way the human brain processes information, and it's an important part of deep learning; these networks are structured with interconnected nodes or neurons, much like the neurons in our brains.
They come in handy for tasks such as recognizing handwriting and identifying faces. On the other hand, artificial intelligence (AI) seeks to mimic human cognitive abilities.
These Neural Networks draw inspiration from biological neural networks, forming a bridge between the natural and artificial. Learning within these networks involves adjusting the weights of connections, a process categorized into three main types: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning.
There are nine different types of neural networks, each with its unique characteristics. These include the Perceptron, Forward Neural Network, Multilayer Perceptron, Convolutional Neural Network, Radial Basis Functional Neural Network, Recurrent Neural Network, LSTM – Long Short-Term Memory, Sequence Sequence Models, and Modular Neural Network. We will discuss more about neural networks, biologically inspired cognitive architectures, and, of course, advanced language models in future articles.
Now, here's the kicker – AGI research isn't set in stone. It's more like a shape-shifter. It evolves as we learn more. Researchers have varying opinions on what's the best path to AGI. Some swear by neural networks, while others are all-in on computational neuroscience. It's like having multiple maps for the same journey, and we're not sure which one will get us there fastest.
Theoretical Frameworks
Now that you know the roads, let's talk about the vehicles. In AGI research, these vehicles are the theoretical frameworks – the grand plans on how to build our AI brain.
High-Level Approaches: Think of these as the blueprints for AGI. There are a few ways we can tackle this beast.
One approach is symbolic. It's all about the power of symbols and how they help us generalize. Imagine if you had a magic dictionary that understood everything in the world. You'd use symbols (like words) to make it understand. Symbolic thought is like the secret language of AGI – it's how we teach it to learn broadly.

Then there's the emergentist approach. It's like watching ants build a complex anthill. Each ant doesn't know the big picture, but together, they create something impressive. Emergentist AGI believes that we can build intelligence by letting simple things (like neurons in our brains) interact and self-organize. It's like the hive mind of AI.
Now, meet the hybrid approach. It's like a mixed bag of candy – you get a bit of everything. In AGI, hybrid systems combine different parts and principles to create something smarter than the sum of its parts. It's like having a toolbox with various tools for different jobs, and AGI knows which one to pick.
Finally, we have the universalist approach. This is the math wizard of AGI. It believes that if we crack the code of AGI in theory, we can scale it down to reality. It's like saying, "Once you understand how to build a bicycle, you can make a whole fleet." Universalist AGI focuses on the math behind intelligence.
The AGI Timeline
Predictions and Expectations
So, when are we getting AGI? Buckle up because opinions on this vary more than toppings on a pizza.

Louis Rosenberg is optimistic. He's the CEO and chief scientist of Unanimous AI, and he boldly predicted back in 2020 that AGI would be achieved by 2030. That's just around the corner in AI terms.

Then there's Jürgen Schmidhuber, co-founder and chief scientist at NNAISENSE. He's eyeing AGI around 2050. That's a bit further down the road, but still within some of our lifetimes.

Now, meet Ray Kurzweil, Google's director of engineering. He's been a pioneer in pattern recognition technology, and his crystal ball says AI will hit "human levels of intelligence" by 2029. And here's the big one: he thinks it will surpass human intelligence by 2045. It sounds like science fiction, right?
But hold on because not everyone's on the same page. Some folks believe AGI is like chasing a rainbow – it might look close, but you'll never catch it. They argue that AGI isn't even possible, given the complexity of human intelligence.
Ethical Considerations & Regulations of AGI
Now, let's talk ethics. AGI might be super smart, but can it tell right from wrong? That's the million-dollar question.

You see, there's a concern that AGI might not fully grasp human ethics and values. It's like trying to teach a fish to understand algebra – it just doesn't compute. And when AGI doesn't get human ethics, it can lead to some serious problems.

Biases, my friend. They're like the bugs in AGI's code. Take advanced tech like ChatGPT, for example. It's been caught spitting out biased and even offensive stuff. That's not what we want from our super-smart AI pals.

So, here's the deal. We've got to be super careful. We need AGI to be on our side, not working against us. Developing AGI for the greater good is the name of the game. We don't want AGI making decisions that harm folks or discriminate against anyone.
Is GPT-4 by OpenAI already showing signs of Artificial General Intelligence?
Is GPT-4 by OpenAI already showing signs of Artificial General Intelligence? Wel, the answer is a bit more complicated than a yes or no. AI researchers are breaking new ground with large language models (LLMs), and GPT-4 is leading the way.
This model, trained on an unprecedented scale by OpenAI, signals a shift towards more general intelligence in LLMs. GPT-4 doesn't just excel in language; it tackles tasks in mathematics, coding, vision, medicine, law, and psychology, often rivaling human-level performance. While it's considered an early version of artificial general intelligence (AGI), understanding its limitations and navigating the challenges ahead are vital.
Could a new approach beyond next-word prediction be the key? This journey is documented in a 155-page paper titled "Sparks of Artificial General Intelligence: Early experiments with GPT-4." Microsoft AI scientists have also noted GPT-4's human-level intelligence, with its staggering 1.7 trillion parameters driving complexity.
Where does this leave us in the grand scheme of things?
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), or the dream of creating software that thinks and learns like us, is still a work in progress. It's like aiming to build a robot that can ace a calculus test, write a beautiful symphony, and whip up a gourmet meal – all on its own.
But AGI isn't just about showing off. It holds the promise of revolutionizing our world. Think about it. If we can crack the AGI code, we could have AI pals that help us find cures for chronic diseases, tackle massive infrastructure problems, and who knows what else?
But one thing's for sure – AGI is a journey worth taking. It's like exploring uncharted territory, full of challenges and mysteries waiting to be unraveled.
In the end, AGI isn't just about building super-smart machines. It's about shaping the future, one line of code at a time. So, as we navigate the twists and turns of AGI's development, one question remains: Are we ready for what lies ahead?













